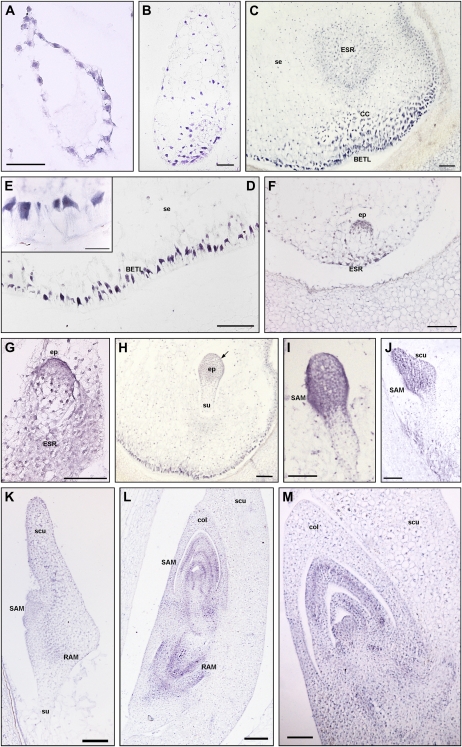
Figure 2.
In situ hybridization of ZmPIN1 mRNAs during maize kernel development. All the images represent longitudinal sections of B73 inbred kernels labeled with an antisense mRNA probe that hybridizes to all three ZmPIN1 transcripts. As soon as the double fertilization occurs, ZmPIN1 genes start to be expressed around the free dividing nuclei that form the syncytium (A), while at the end of cellularization phase, the endosperm shows a gradient of ZmPIN1 expression. The transcripts are most abundant in the basal part of the endosperm (B), a region that will differentiate in the BETL domain and in the cells of the ESR. At the end of differentiation, both these domains show a high expression of ZmPIN1 (C). In BETL cells, ZmPIN1 transcripts are very abundant and compartmentalized on the inner side of the cells (D and E); they also mark the above-located conductive cells (C). In the ESR domain, the ZmPIN1 hybridization signal is particularly strong during early stages of embryogenesis (C, F, and G). During embryogenesis, ZmPIN1 mRNAs are mainly expressed in the embryo proper at the proembryo stage (F and G). Later on, at the early transition stage, ZmPIN1 transcripts mark both the central group of cells in the embryo proper and the differentiating protoderm (H), while no ZmPIN1 expression is detectable in the suspensor (H). The arrow in H indicates the protoderm layer. During the late transition stage, ZmPIN1 mRNAs are mainly localized on the adaxial surface where SAM bulges out (I) and in the scutellum tip (J), whereas very weak hybridization signal is detectable on the scutellum abaxial side (J). A high expression of ZmPIN1 is detectable in the scutellum provascular tissues and in the RAM (K). During the morphogenetic phase, SAM produces five to six leaf primordia and ZmPIN1 genes are expressed in the corpus of the SAM, in the developing primordia, and in the vasculature of the differentiated leaves (L and M). The signal is still present in the RAM and coleorhiza (L). CC, Conductive cells; col, coleoptile; ep, embryo proper; scu, scutellum; se, starchy endosperm; su, suspensor. Bars = 200 μ m in L; 100 μ m in C, G, H to K, and M; 50 μ m in A, B, D, and F; and 25 μ m in E.