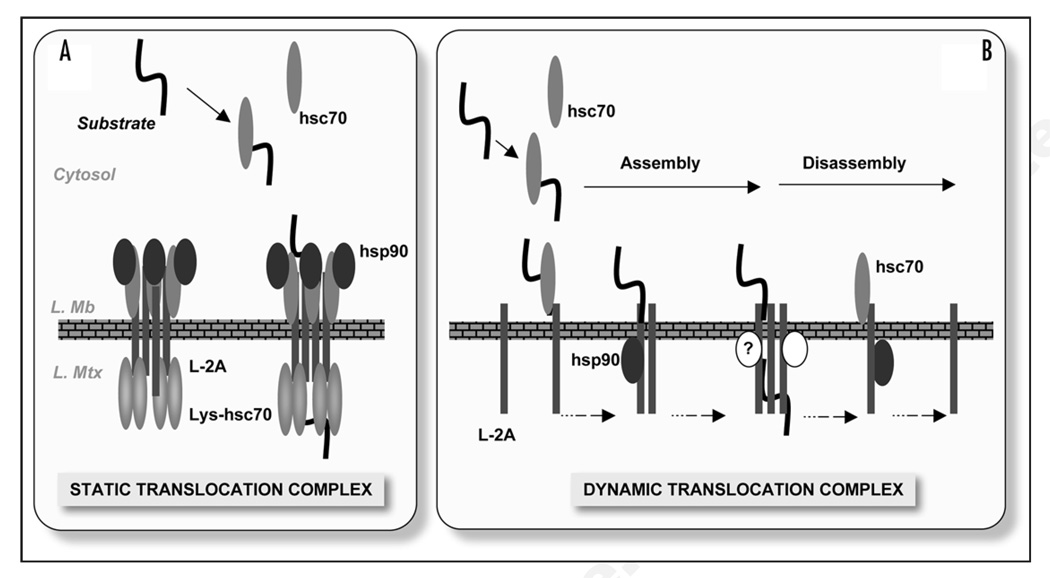
Figure 1.
CMA translocation at the lysosomal membrane. (A) Hypothetical model of the CMA translocation complex at the lysosomal membrane by analogy to the transport systems in other organelles. The translocation complex was conceived as a stable structure organized around multiple LAMP-2A (L-2A) molecules flanked by chaperones on both sides of the lysosomal membrane (L. Mb). Substrates bind to the exposed cytosolic tails, and chaperones facilitate substrate unfolding and translocation across the membrane and into the lysosomal matrix (L. Mtx). (B) Model of the CMA translocation complex proposed as a result of our recent studies.8 Substrate proteins bind to monomers of LAMP-2A, which progressively organize into a multimeric complex that facilitates delivery of substrate proteins to the lumen. Lysosomal chaperones, hsc70 and hsp90, interact with LAMP-2A when present in intermediate complexes formed during assembly and disassembly of the translocation complex. Other yet to be identified proteins (?) could also contribute to the formation of this translocation complex at the lysosomal membrane.