Abstract
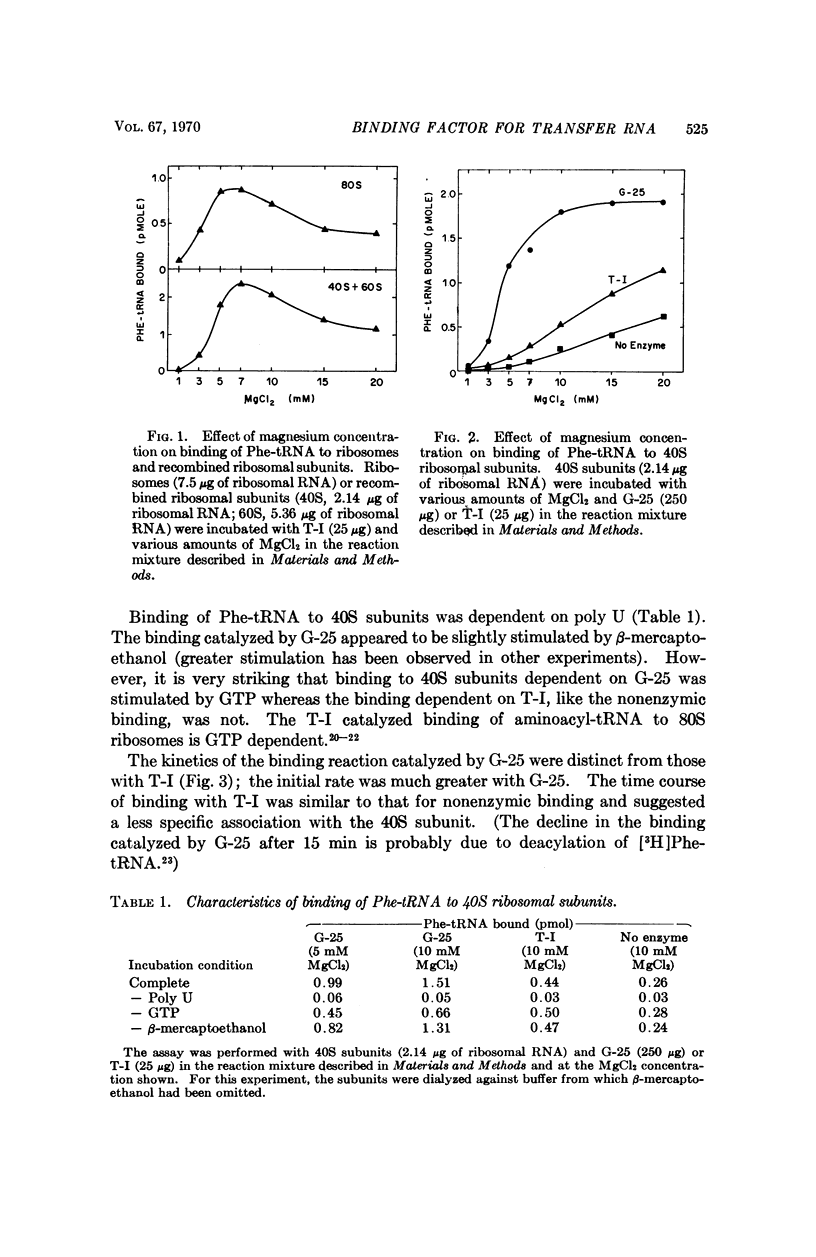
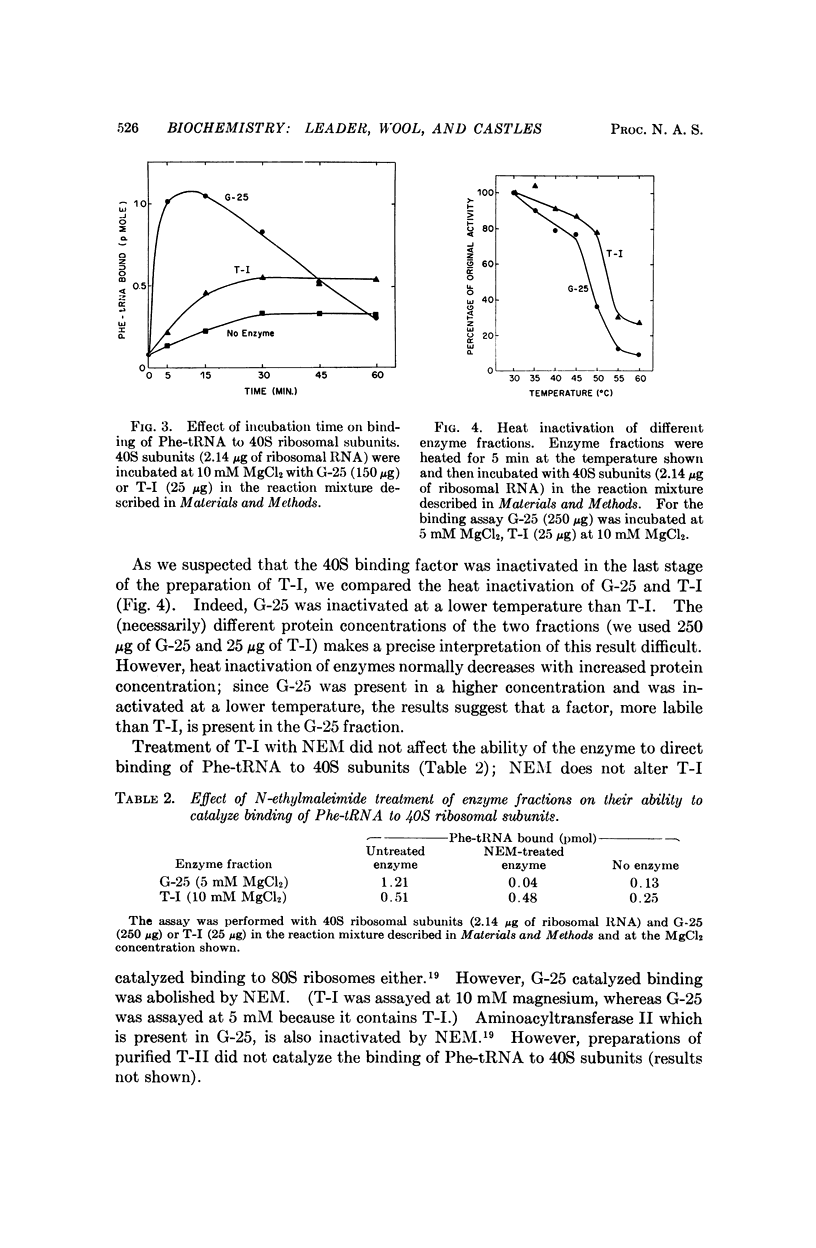
A factor present in rat liver supernatant catalyzes binding of Phe-tRNA to 40S ribosomal subunits from rat skeletal muscle. This factor could be distinguished from aminoacyltransferase I by a number of criteria: (1) at lower concentrations of magnesium (5 mM) the 40S binding factor was approximately seven times as effective as T-I in catalyzing binding of Phe-tRNA to 40S subunits; (2) the kinetics of the binding reaction were different when catalyzed by the 40S binding factor, in particular the initial rate was greater than in the presence of T-I—indeed, the kinetics of the T-I catalyzed reaction resembled nonenzymic binding; (3) GTP was required for maximal binding of Phe-tRNA to 40S subunits in the presence of the 40S binding factor, but not for the T-I catalyzed reaction; (4) the 40S binding factor was inactivated by N-ethylmaleimide whereas T-I was not; (5) finally, the 40S binding factor was more susceptible to heat inactivation. Binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to 40S ribosomal subunits may be a paradigm for the initiation of protein synthesis, and the 40S binding factor may play a role in the process.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. C., Smith A. E. Initiator codons in eukaryotes. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):610–612. doi: 10.1038/226610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castles J. J., Wool I. G. Polyuridylic acid directed binding of phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid to mammalian 40S ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1970 Apr 28;9(9):1909–1916. doi: 10.1021/bi00811a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibuki F., Moldave K. Evidence for the enzymatic binding of aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid to rat liver ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 25;243(4):791–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R. Ribosomal subunit exchange in the cytoplasm of a eukaryote. Nature. 1969 Jun 7;222(5197):950–953. doi: 10.1038/222950a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laycock D. G., Hunt J. A. Synthesis of rabbit globin by a bacterial cell free system. Nature. 1969 Mar 22;221(5186):1118–1122. doi: 10.1038/2211118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew C. C., Haslett G. W., Allfrey V. G. N-acetyl-seryl-tRNA and polypeptide chain initiation during histone biosynthesis. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):414–417. doi: 10.1038/226414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., McKeehan W. L., Culp W., Hardesty B. Partial characterization of the enzymatic properties of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4340–4350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcker K. A., Smith A. E. On the universality of the mechanism of polypeptide chain initiation. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1969;51(10):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. E., Rolleston F. S., Low R. B., Wool I. G. Dissociation and reassociation of skeletal muscle ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. E., Wool I. G. Formation of active hybrids from subunits of muscle ribosomes from normal and diabetic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):569–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Hardesty B. Purification and partial characterization of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding enzyme from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4330–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Schweet R. Isolation of a protein fraction from reticulocyte ribosomes required for de novo synthesis of hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):632–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90622-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Lowry C. V. PHAGE f2 RNA-DIRECTED BINDING OF FORMYLMETHIONYL-TRNA TO RIBOSOMES AND THE ROLE OF 30S RIBOSOMAL SUBUNITS IN INITIATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):946–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. II. A possible site on the 50 S subunit protecting aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid from deacylation. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4939–4947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard P. M., Gilbert J. M., Shafritz D. A., Anderson W. F. Factors for the initiation of haemoglobin synthesis by rabbit reticulocyte ribosomes. Nature. 1970 May 9;226(5245):511–514. doi: 10.1038/226511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P., Moldave K. Interaction of polypeptide chain elongation factors with rat liver ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 28;46(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M., Mosteller R. D., Hardesty B. NaF inhibition of the initial binding of aminoacyl-sRNA to reticulocyte ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):701–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneir M., Moldave K. The isolation and biological activity of multiple forms of aminoacyl transferase I of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):58–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Marcker K. A. Cytoplasmic methionine transfer RNAs from eukaryotes. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):607–610. doi: 10.1038/226607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Marcker K. A. N-formylmethionyl transfer RNA in mitochondria from yeast and rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec 14;38(2):241–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90409-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley W. M., Jr, Salas M., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message: factors involved in the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):290–295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


