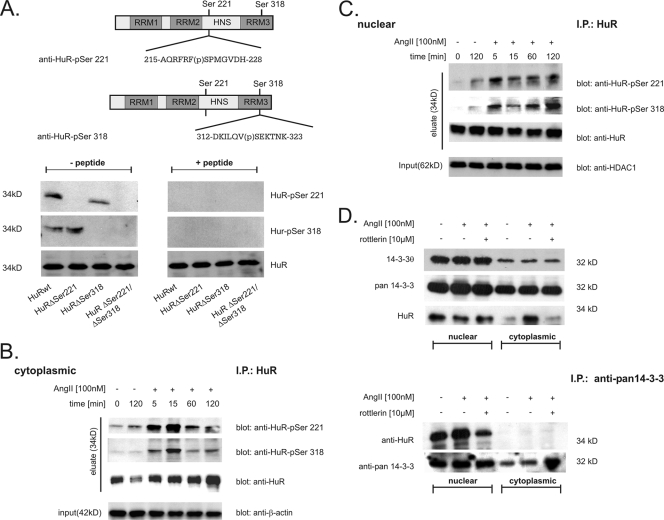
FIG. 4.
HuR is phosphorylated in vivo at serines 221 and 318 in a time-dependent manner. (A) Upper panel, schematic overview of HuR and serines critically involved in PKCδ-dependent HuR phosphorylation. Sequences of peptides used for generation of the indicated HuR phosphorylation-specific antibodies and the positions of phosphorylated (p) serine residues are indicated. Lower panel, for cell-free in vitro phosphorylation assays, the indicated HuR proteins were incubated with PKCδ for 10 min at 32°C and processed for Western blot analysis. Phosphorylation of HuR at Ser 221 (HuR-pSer221) and Ser 318 (HuR-pSer318) in comparison with unphosphorylated HuR (HuR) was monitored by successive incubation with either of the depicted phospho-specific antibodies and a commercial antibody against total HuR as indicated. Both phospho-specific HuR antibodies (anti-HuR-pSer221 and anti-HuR-pSer318) were preincubated on ice for 30 min without (− peptide) or with (+ peptide) 5 μg of the peptide used for immunization before being subjected to PAGE. (B and C). HMC were serum starved overnight and subsequently treated with vehicle (−) or with AngII (100 nM, +) for the indicated times before cells were lysed for cytoplasmic (B) and nuclear (C) fractions. For IP of HuR, a total protein amount of 500 μg from each fraction was incubated overnight with 2 μg of anti-HuR antibody (IP: HuR), and HuR precipitates were assessed by Western blot analysis by successive incubation with the indicated antibodies (eluate). To ascertain equal protein contents within the fractions, the blots were stripped and reprobed with either an anti-β-actin (input in panel B) or anti-HDAC-1 (input in panel C) antibody. AngII increases association of nuclear HuR with 14-3-3 proteins. (D) Upper panel, AngII-induced increase in cytoplasmic HuR level is not accompanied by a change in the intracellular redistribution of 14-3-3θ and pan-14-3-3. Serum-starved HMC were treated with vehicle (−), AngII (+), or AngII plus the PKCδ-specific inhibitor rottlerin (10 μM) for 2 h before cells were lysed for nuclear extracts and cytoplasmic fractions. Subsequently, different cell fractions from HMC were successively probed with the indicated antibodies. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments giving similar results. Lower panel, for IP, a total protein amount of 200 μg of either nuclear or cytoplasmic extract was incubated overnight with 2 μg of a pan-specific 14-3-3 antibody (IP: anti-pan 14-3-3), and precipitates were subsequently analyzed by Western blot analysis using an anti-HuR-specific antibody. To confirm equal amounts of input protein, the IPs were reprobed with the anti-pan 14-3-3 antibody as indicated.