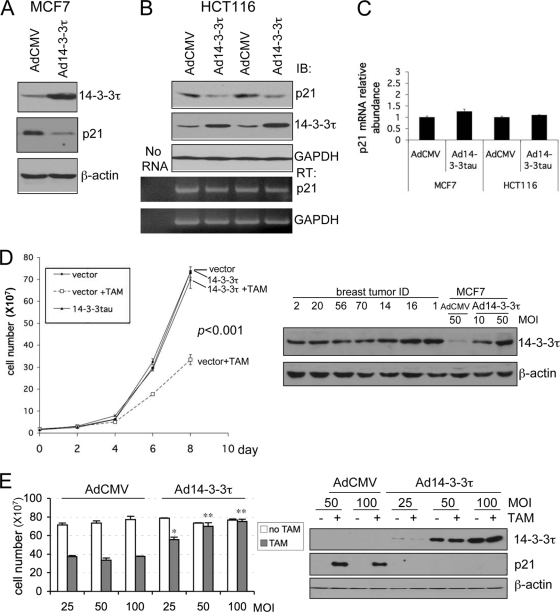
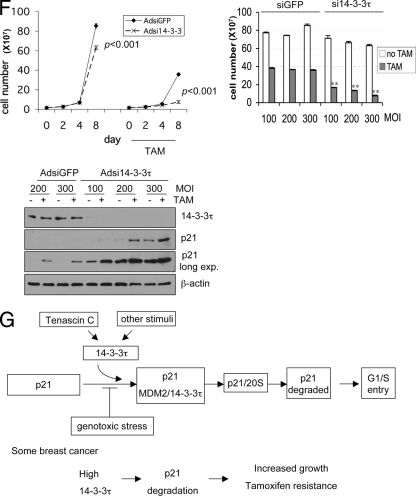
FIG. 11.
Role for 14-3-3τ in the response to tamoxifen in MCF7 breast cancer cells. (A to C) MCF7 cells (A) or HCT116 cells (B) were infected with AdCMV or Ad14-3-3τ at a multiplicity of infection of 40. Forty-eight hours later, cells were harvested for Western blot and RT-PCR analyses. The results of two independent experiments with AdCMV and Ad14-3-3τ infection are shown (B). (C) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR of p21 transcript levels for MCF7 or HCT116 cells (A and B, respectively). (D) MCF7 cells were infected with AdCMV or Ad14-3-3τ at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 50. Two days later, the cells were either treated with tamoxifen (TAM) at 5 μM or a dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle control. The cells were split, reinfected, and counted every 2 days. The data represent the mean cell numbers ± standard deviations for three independent samples for each arm. The difference is significant (P < 0.001), according to the generalized estimating equations (GEE) model. (Right panels) Western blot analysis of cell lysates from the experiment whose results are presented in the left panel of panel D and from breast tumor tissue lysates described in Fig. S6 in the supplemental material. (E) MCF7 cells were infected with AdCMV or Ad14-3-3τ at a multiplicity of infection of 25, 50, or 100 every 2 days and were treated with tamoxifen for 8 days. Cell numbers were counted or analyzed by Western blotting (right panels). *, P ≤ 0.01 compared with the results obtained with AdCMV at the same multiplicity of infection; **, P < 0.001 (t test) compared with the results obtained with AdCMV at the same multiplicity of infection. The results of parallel experiments with tamoxifen treatment for 6 days are presented in Fig. S9 in the supplemental material. (F) MCF7 cells were infected with AdsiGFP or Adsi14-3-3τ at a multiplicity of infection of 100, 200, or 300. Two days later, the cells were treated with either tamoxifen at 5 μM or the dimethyl sulfoxide vehicle control. The cells were split, reinfected, and counted. The data represent the mean the cell numbers ± standard deviations for three independent samples for each arm. (Left panel) The results of infection at a multiplicity of infection of 300. The P values are based on the paired two-tailed t test. (Right panel) The results of infection at a multiplicity of infection of 100 to 300 and following tamoxifen treatment for 8 days. **, P < 0.001 (t test) compared with the results obtained with siGFP at the same multiplicity of infection. (Lower panel) The cell lysates from cells treated with tamoxifen for 8 days were analyzed by Western blotting. (G) A model for the role of 14-3-3τ in the regulation of p21 protein turnover. In response to cellular stimuli such as tenascin-C signaling, 14-3-3τ is induced. Then, 14-3-3τ, along with MDM2, promotes the ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of p21 and induces cell cycle progression. The interaction between 14-3-3τ and p21, however, is inhibited upon genotoxic stress. When 14-3-3τ levels are abnormally elevated in breast cancer, these events may lead to the degradation of p21 and cause resistance to tamoxifen or an enhanced growth property.