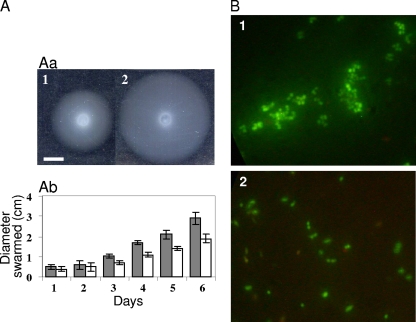
FIG. 7.
hfq regulates physiological responses to changes in environment. (A) The S. meliloti hfq mutant swarms less efficiently than the wild-type strain. (Aa) Five-day colonies from the hfq mutant Smblφ500 (panel 1) and the WT (panel 2) strains were plated on a swarming plate (0.3% agar) and incubated at 30°C. The white bar represents 0.5 cm. (Ab) Results of swarming for the WT (gray bars) and the hfq mutant (white bars) strains. Colony progression was measured every day. The bars represent the means of results from 3 experiments. (B) When hfq mutant cultures (panel 1) in GAS medium were maintained for 1 month, aggregates were observed. Similar aggregates were not observed in WT cells (panel 2).