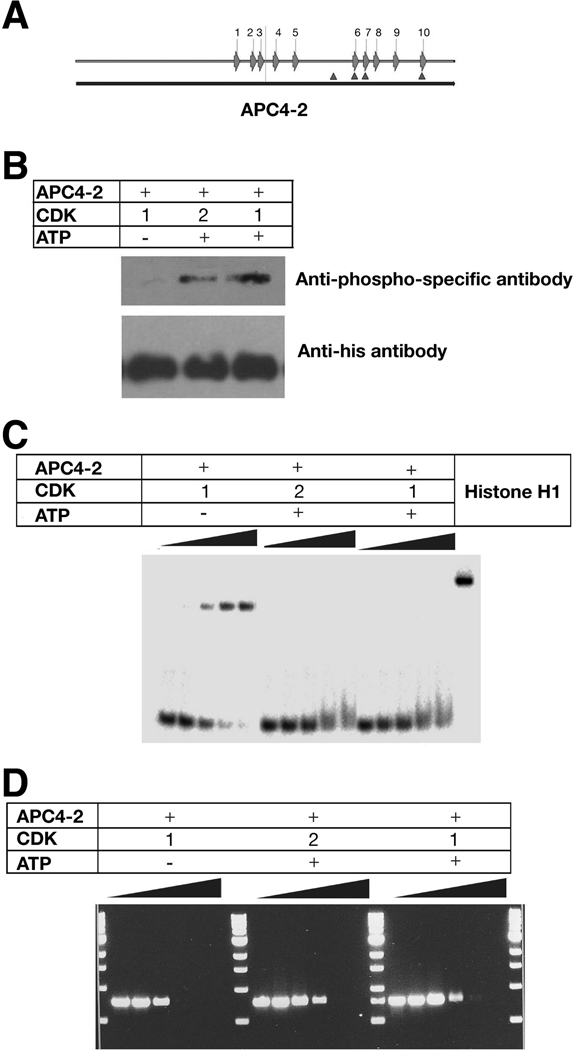
Figure 6. CDK phosphorylation of APC reduces DNA binding and inhibition of replication.
A. Schematic diagram of S(T)PXX binding motifs and CDK consensus phosphorylation sites within APC4-2. Arrows represent S(T)PXX binding motifs and triangles represent CDK consensus phosphorylation sites.
B. Western results of APC 4-2 phosphorylation by CDKs. Purified APC4-2 proteins were incubated with CDK1 or 2 in the absence (control) and presence of ATP, separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and probed with a anti-phospho-threonine-proline monoclonal antibody (upper panel) or a monoclonal anti-His antibody (lower panel).
C. Gel mobility shifts of radioactively labeled oligonucleotides in the presence of phosphorylated or nonphosphorylated APC4-2. A radiolabelled 60-base single-stranded oligonucleotide (2 nM) was incubated with the corresponding proteins, separated by 8% PAGE and analyzed by phosphorimager. The protein concentrations for each sample are: 0, 50, 75, 100, and 125 nM, respectively.
D. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products prepared in the presence of phosphorylated or nonphosphorylated APC4-2 at different quantitative ratio of [protein]/[DNA] as in Figure 3A. PCR products were separated using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by ethidium bromide staining.