Abstract
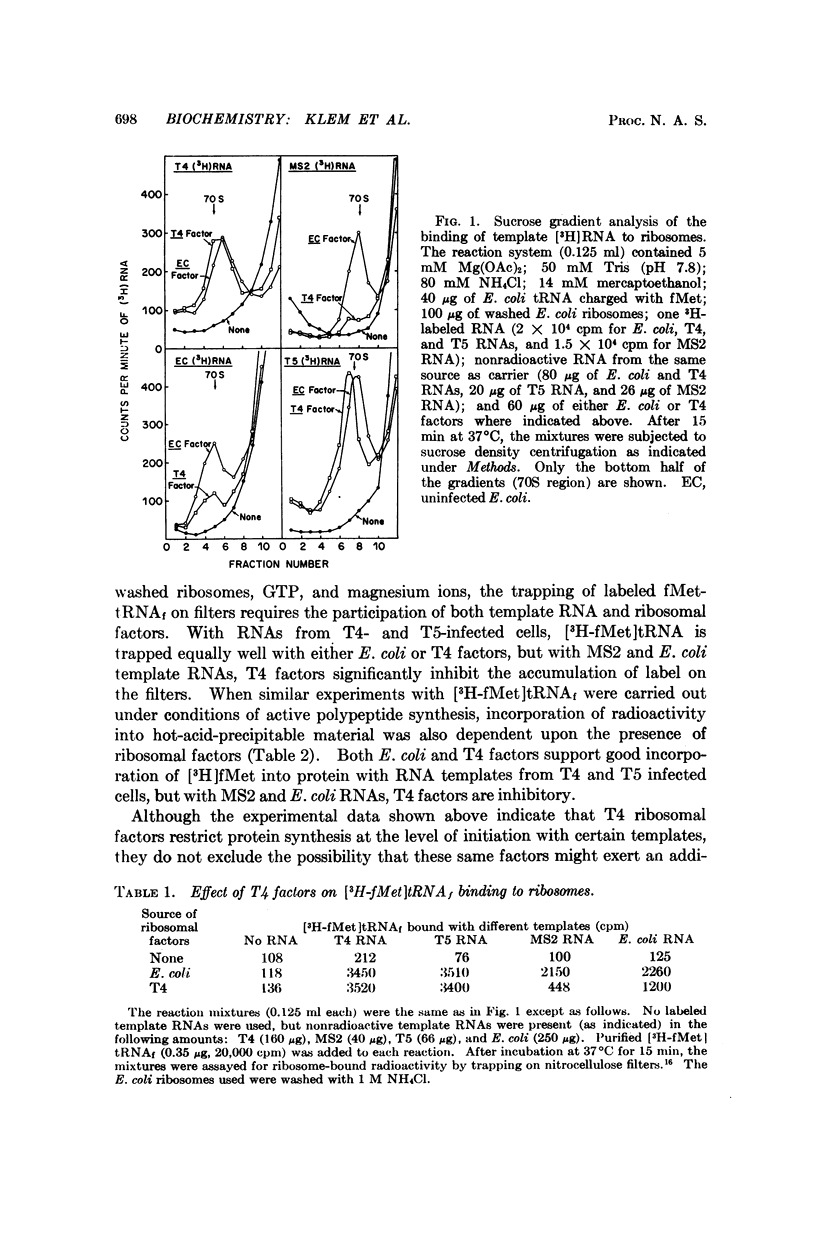
The phenomenon of selective translation of T4 template RNA by ribosomes from T4-infected cells, or factors derived therefrom, has been extended to studies on the initiation of protein synthesis. A high-salt extract derived from T4-infected ribosomes inhibits the formation of initiation complexes of MS2 and Escherichia coli template RNA with uninfected ribosomes while efficiently supporting the formation of initiation complexes with T4 template RNA. T4 factors also permit T5 template RNA to bind to E. coli ribosomes, which indicates that the T4 selective effect is not exclusive for T4 templates. Other evidence indicates that T4 factors do not alter the process of polypeptide chain elongation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daniel V., Sarid S., Littauer U. Z. Amino acid acceptor activity of bacteriophage T4 transfer RNA. FEBS Lett. 1968 Nov;2(1):39–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(68)80095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube S. K., Rudland P. S. Control of translation by T4 phage: altered binding of disfavoured messengers. Nature. 1970 May 30;226(5248):820–823. doi: 10.1038/226820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER D., JERREL E. A. The amino acid composition of T3 bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P., Stewart M. L. Inhibition of the attachment of messenger ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):719–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Hofschneider P. H. Interference of bacteriophage T4 in the reproduction of RNA-phage M12. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):173–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. T., Foft J. W., Weiss S. B. Effect of bacteriophage infection on the sulfur-labeling of sRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2028–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. T., Weiss S. B. Selective translation of T4 template RNA by ribosomes from T4-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):345–351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki K., Sabol S., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message. VII. Role of initiation factors in formation of the chain initiation complex with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano-Sueoka T., Sueoka N. Modification of leucyl-sRNA after bacteriophage infection. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):183–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Earhart C. F. Phage-induced appearance of a valyl sRNA synthetase activity in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:557–563. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., KANO-SUEOKA T. A SPECIFIC MODIFICATION OF LEUCYL-SRNA OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AFTER PHAGE T2 INFECTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1535–1540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl P. D., Singer R. E., Conway T. W. A factor required for the translation of bacteriophage f2 RNA in extracts of T4-infected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):631–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolarsky M., Tal M. Novel method for measuring polyuridylic acid binding to ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Dube S. K., Rudland P. S. Control of translation of T4 phage: altered ribosome binding at R17 initiation sites. Nature. 1970 May 30;226(5248):824–827. doi: 10.1038/226824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Smith D. W. The effect of bacteriophage T2 infection of the synthesis of transfer RNA in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1968 Oct;36(2):212–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainfan E., Srinivasan P. R., Borek E. Alterations in the transfer ribonucleic acid methylases after bacteriophage infection or induction. Biochemistry. 1965 Dec;4(12):2845–2848. doi: 10.1021/bi00888a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Novelli G. D. A new change in leucine transfer RNA observed in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):979–985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. B., Hsu W. T., Foft J. W., Scherberg N. H. Transfer RNA coded by the T4 bacteriophage genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):114–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J. M., Haselkorn R. The chain growth rate of T4 lysozyme in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):388–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


