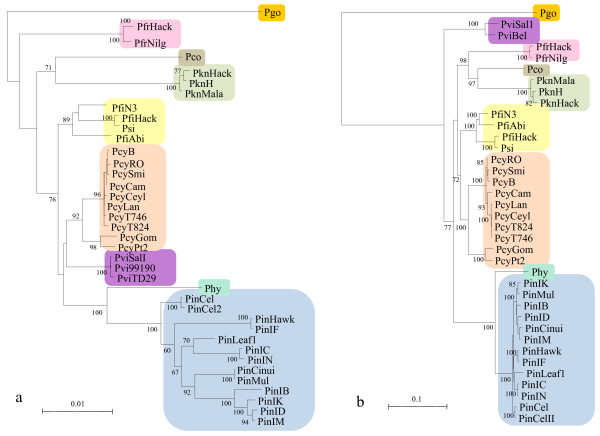
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic trees of the mitochondrial genome and msp1 of P. vivax and P. vivax-related simian malaria parasite species. (a) The maximum-likelihood (ML) tree of the mitochondrial genome. Aligned sequences of the mitochondrial genome (5818 bp) from P. vivax and related simian malaria parasite species were used for constructing the tree with 100 heuristic replicates under the GTR + I + G model with an α = 0.812. (b) The ML tree of the msp1 gene. The aligned 4176 bp (Additional file 3) sequences were used for constructing the tree with 100 heuristic replicates under the GTR + I + G model with an α = 0.866. Abbreviations of species and strains are: Pgo = P. gonderi, Pfr = P. fragile, Pco = P. coatneyi, Pkn = P. knowlesi, Pfi = P. fieldi, Psi = P. simiovale, Pcy = P. cynomolgi, Pvi = P. vivax, Phy = P. hylobati, and Pin = P. inui; and Hack = Hackeri, Nilg = Nilgiri, Mala = Malayan, N3 = N-3, Abi = A.b.introlatus, Smi = Smithsonian, Cam = Cambodian, Ceyl = Ceylonensis, Lan = Langur, Gom = Gombak, SalI = Sal-I, Bel = Belem, Cel = Celebes, CelII = Celebes II, Hawk = Hawking, Leaf1 = Leaf monkey #1, Mul = Mulligan. In both (a) and (b), only bootstrap values = 60% are indicated at nodes.