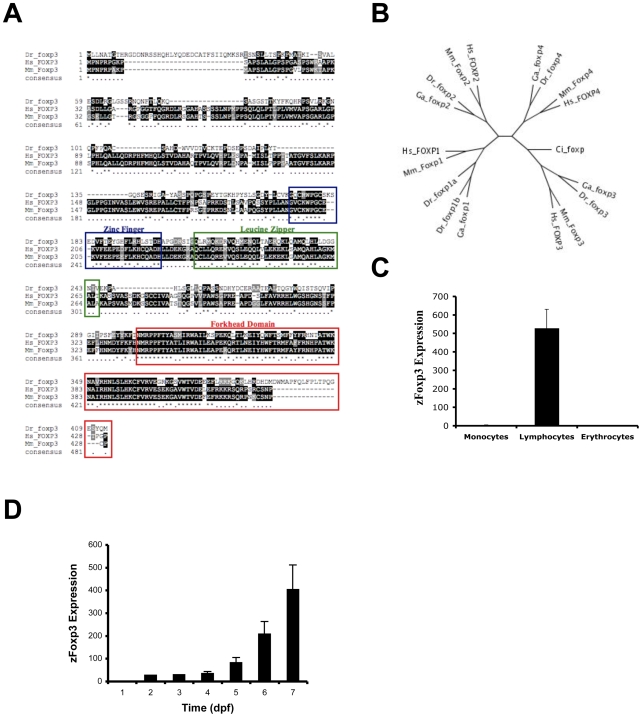
Figure 2. Zebrafish Foxp3 (zFoxp3).
(A) Sequence comparison of putative FoxP3 genes of zebrafish, human and mouse. The stars indicate identity, dashes were introduced for optimal alignment. The zinc finger, leucine zipper and forkhead domains are highlighted with a blue, green or red box, respectively. (B) Radial gene tree showing the Foxp1, Foxp2, Foxp3 and Foxp4 proteins in mammals and fish, where the Ciona intestinalis Foxp sequence is the outgroup. The branch lengths are proportional to the distance between the sequences. Mm, Mus musculus; Hs, Homo sapiens; Dr, Danio rerio; Ga, Gasterosteus aculeatus (stickleback); Ci, Ciona intestinalis. The accession numbers for the amino acid sequences used in the gene tree analysis are as follows: Danio rerio Foxp1a Q08BX8 BC124513; Foxp1b Q2LE08 NM_001039637; Foxp2 Q4JNX5 NM_001030082; Foxp3 annotated (EST CK028390); Foxp4 annotated. Homo sapiens: Foxp1 Q9H334 NM_001012505, Foxp2 O15409 NM_148899, Foxp3 Q9BZS1 NM_014009, Foxp4 Q8IVH2 NM_138457; Mus musculus: Foxp1 P58462 NM_053202, Foxp2 P58463 NM_053242, Foxp3 Q99JB6 NM_054039, Foxp4 Q9DBY0 NM_028767; Ciona intestinalis Foxp Q4H3H6. The amino acid sequence of the apparent stickleback orthologues of Foxp1, Foxp2, Foxp3 and Foxp4 were obtained from Ensembl. (C) Monocytes, lymphocytes and erythrocytes were sorted by FACS and the expression of zFoxP3 was determined by real time PCR (mean + s.d. of triplicates). (D) zFoxp3 and GAPDH were quantified by qPCR on cDNA prepared from zebrafish embryos at different times after fertilization. Two independent experiments produced similar results.