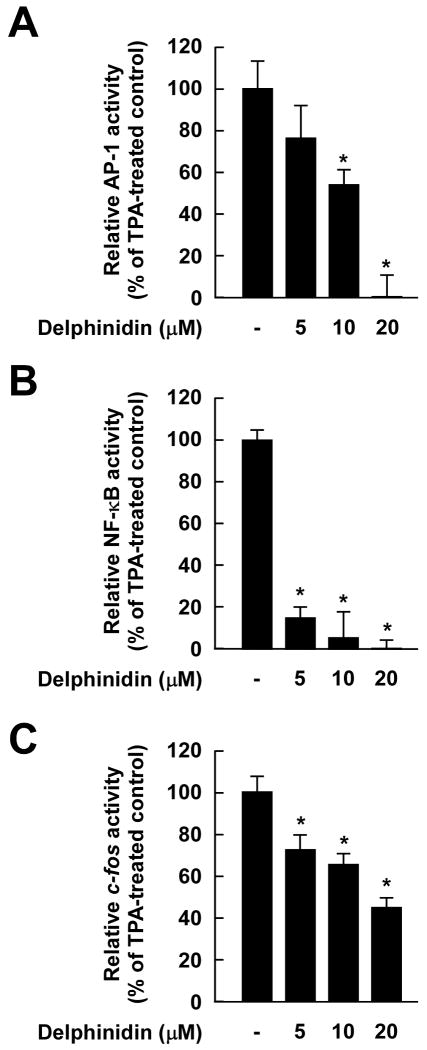
Fig. 3.
Effects of delphinidin on TPA-induced AP-1 and NF-κB transactivation and c-fos promoter activity in JB6 P+ cells. A and B, Delphinidin inhibits TPA-induced AP-1 (A) and NF-κB (B) transactivation. The JB6 P+ cells, which were stably transfected with an AP-1 or NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmid, were pretreated with delphinidin for 1 h at the indicated concentrations (0, 5, 10, 20 μM) before being exposed to TPA for 24 h. The relative activity was measured by a luciferase assay as described in “Materials and Methods”. Data are presented as mean and S.D. values of the AP-1 and NF-κB luciferase activities from three independent experiments. For A and B, the asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.01) between groups treated with TPA and delphinidin and the group exposed to TPA alone. C, Delphinidin suppresses TPA-induced c-fos promoter activity. For the reporter-gene assay, JB6 P+ cells were transfected with a plasmid mixture containing the c-fos luciferase reporter gene (0.5 μg) and the pRL-SV40 gene (0.5 μg). At 24 h after transfection, cells were starved for 24 h by incubation in 0.1% FBS/MEM at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Cells were then treated with delphinidin at the indicated concentrations (0, 5, 10, 20 μM) for 1 h before being exposed to TPA for 12 h. Firefly luciferase activity was determined in cell lysates and normalized to Renilla luciferase activity, and c-fos luciferase activity is expressed relative to control cells not exposed to TPA. Data are presented as mean and S.D. values of the c-fos luciferase activity from three independent experiments. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.01) between groups treated with TPA and delphinidin and the group exposed to TPA alone.