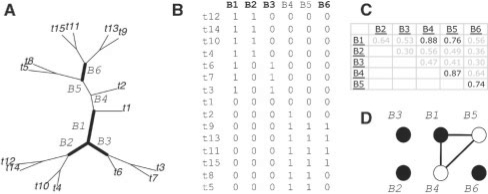
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the bipartition selection procedure. (A) A phylogeny with 15 leaves. (B) The matrix of six bipartitions with size threshold of at least three leaves on either side of the bipartition. (C) The pairwise absolute correlation matrix. (D) The corresponding instance to the minimum dominating set problem using correlation threshold 0.7. Black vertices (1, 2, 3, 6) form the solution returned by the greedy algorithm; bipartitions corresponding to the four vertices are also emboldened in the phylogeny (A) and labeled in boldface in the matrix of bipartitions (B). Note that because each vertex in (D) is adjacent to at least one black vertex, this ensures each of the six bipartitions is correlated with at least one of the four chosen bipartitions, so the reduced set of bipartitions still represents the topology of the original phylogeny well.