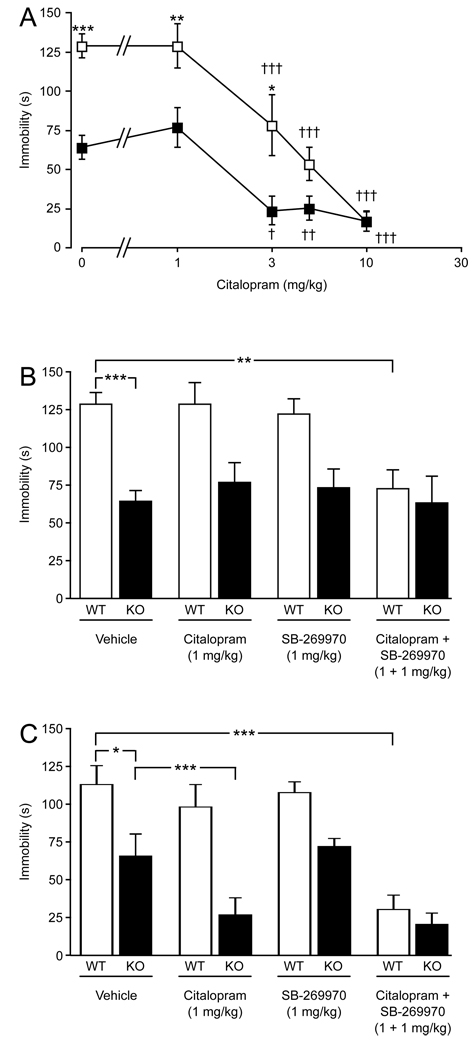
Fig. 1.
Effects of citalopram on mouse behavior in the tail suspension and forced swim tests. (A) Dose-response effect of citalopram on the immobility profile of 5-HT7+/+ (□) and 5-HT7−/− (■) mice in the tail suspension test. (B) Effects of individual and concurrent injections of 1 mg/kg citalopram and 1mg/kg SB-269970 in the tail suspension test in 5-HT7+/+ (WT) and 5-HT7−/− (KO) mice. (C) Effects of individual and concurrent injections of 1 mg/kg citalopram and 1 mg/kg SB-269970 in the forced swim test in 5-HT7+/+ (WT) and 5-HT7−/− (KO) mice. Values are mean ± SEM. n = 8–10 animals per genotype per treatment group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 between the genotypes (A) or indicated groups (B, C); †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01, †††P < 0.001 within a genotype compared to control; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-hoc test.