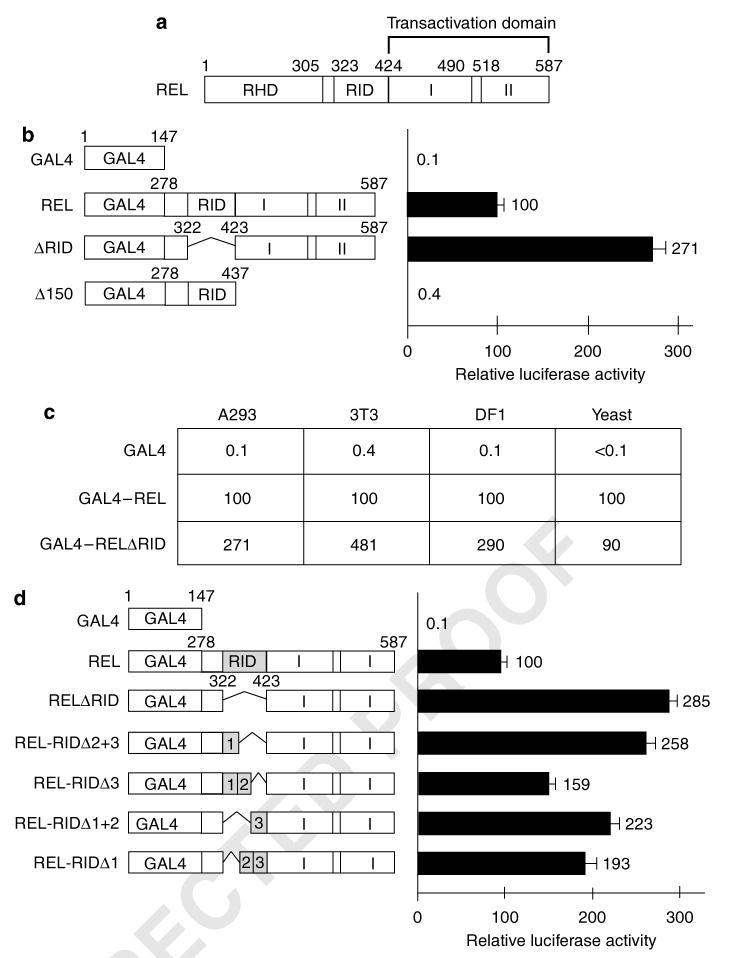
Figure 1.
Deletion of REL residues 323–422 enhances transactivation by REL in vertebrate cells. (a) The general structure of REL is shown at the top (RHD, Rel homology domain; RID, REL inhibitory domain; I and II, transactivation subdomains I and II). (b and d) GAL4 fusion proteins containing the indicated REL sequences were analysed for their abilities to activate transcription from a GAL4 site-containing luciferase reporter in A293 cells. Values are relative to those seen with GAL4–REL (100) and are the averages of three experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars indicate s.e. (c) The indicated GAL4 fusion proteins were analysed for their abilities to activate transcription from a GAL4 site-containing reporter in human (A293), mouse (3T3), chicken (DF1) and S. cerevisiae (yeast) cells. Values are relative to GAL4–REL (100). Experiments were performed three times in triplicate in A293 cells and S. cerevisiae and two times in triplicate in mouse 3T3 cells and chicken DF1 cells.