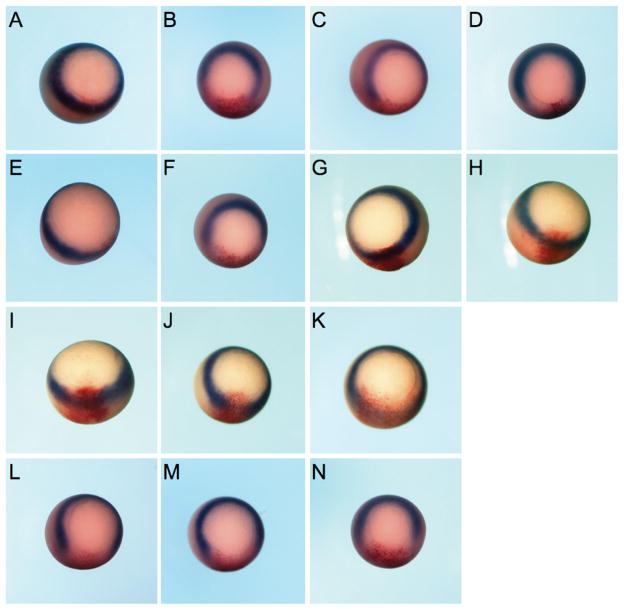
Figure 6.
Endogenous Xenopus brachyury is down-regulated by ectopic expression of Mix.3. Embryos were injected in one blastomere at the two-cell stage with test mRNA together with a β-galactosidase (β-gal) mRNA as a lineage tracer (stained red). In situ hybridization analyses for Xbra expression (stained blue/purple) were performed at early gastrula (Stage 10.5). Representative embryos for each group are shown; the number of embryos examined and the percentage that are the same as the representative are noted below. (A) β-gal alone (100%, n = 61). (B and C) Mix.3. Ectopic expression of Mix.3 results in decreased Xbra expression on the injected side of the embryo (96% have decreased Xbra expression, n = 107/112). (D) M3Δ123. A mutant of Mix.3 that cannot interact with CDK9 maintains Xbra repression activity (100%, n = 21). (E) CDK9. Expression of CDK9 alone does not disrupt Xbra expression in the marginal zone of the embryo (100%, n = 23). (F) Mix.3 + CDK9. CDK9 expression does not block the repression of Xbra expression by Mix.3 (100%, n = 25). (G) Cyclin K (100%, n = 22). (H) Cyclin T2 (100%, n = 23). (I) CDK9 + cyclin K (100%, n = 51). (J and K) CDK9 + cyclin T2. Expression of CDK9 with cyclin T2 disrupts Xbra expression (89%, n = 40/45). (L) Mix.3 + CDK9 + cyclin K (100%, n = 25). (M) Mix.3 + CDK9 + cyclin T2 (100%, n = 44). (N) Mix.3Δ123 + CDK9 + cyclin T2 (98%, n = 46/47).