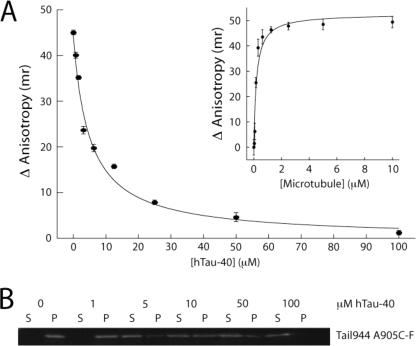
FIGURE 2.
The kinesin-1 tail and Tau compete for the same binding site on microtubules. Tail944 A905C-F binds to microtubules with an affinity of 0.20 ± 0.052 μm in 100 mm NaCl (A, inset), as measured by fluorescence anisotropy. The binding of the same tail construct is inhibited in a concentration-dependent fashion by hTau-40 as measured by fluorescence anisotropy (A) and microtubule co-sedimentation (B, gel shows the amount of bound (P) and free (S) tail in the presence of increasing concentrations of Tau). The solid line in A is a fit to a simple competitive inhibition model (r2 = 0.99), with half-maximal inhibition at 4.9 μm Tau. Fluorescence anisotropy data are reported as the mean ± S.E. for three experiments.