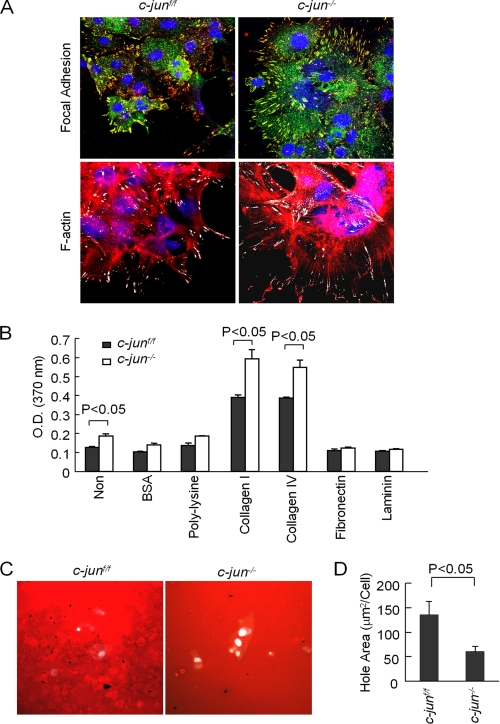
FIGURE 2.
c-Jun reduces mammary epithelial cell adhesion and enhances invadopodia. A, confocal microscopy for focal contacts (tyrosine phosphorylated paxillin in yellow, with nuclei marked by 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole in blue). Stress fiber formation is demarcated by F-actin distribution in cells. Note: Points of focal contact are shown in white. B, cellular adhesion assays comparing c-jun+/+ and c-jun−/− cells plated on distinct substrates. Non, non-cell; BSA, bovine serum albumin. C and D, invadopodia assays were conducted on c-jun+/+ and c-jun−/− MET. Holes indicating active invadapodia are shown in black. The hole area is shown as mean ± S.E. for n = 10 separate images.