FIGURE 2.
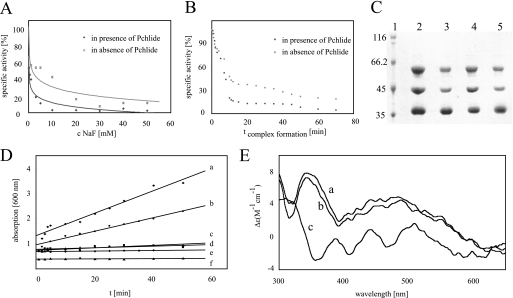
Formation of ternary DPOR complexes is supported by Pchlide, ATPase activity of DPOR catalysis, and circular dichroism spectra of ChlL2. A, DPOR complex formation for 90 min with 10 mm MgADP, 500 μm AlCl3, and increasing concentrations of NaF ranging from 10 μm to 50 mm in the presence (dots) and absence (crosses) of Pchlide. Subsequent DPOR assays indicate the loss of DPOR activity. B, time dependence of DPOR complex formation. DPOR complex formation with MgADP·AlF4− in the presence (dark gray) and absence (light gray) of Pchlide for 1–70 min. Subsequent Pchlide reduction assays indicate the formation of inactive DPOR complexes. C, Pchlide-dependent DPOR complex formation. SDS-PAGE analyses of ternary DPOR complexes containing MgADP·AlF4− (lanes 2 and 3) and ChlLΔLeu153 (lanes 4 and 5), respectively. Lane 1, molecular mass marker, relative molecular masses (×1000) are indicated; lanes 2 and 4, complex formation in the presence of Pchlide; lanes 3 and 5, complex formation in the absence of Pchlide. D, ATPase activity of DPOR was analyzed over 50 min after addition of 500 μm ATP. Absorption at 600 nm indicates liberated phosphate as a green metallocomplex. Analyzed samples contained: a, (ChlN/ChlB)2 and ChlL2 in the presence of Pchlide; b, (ChlN/ChlB)2 and ChlL2 without Pchlide; c, sole ChlL2; d, sole (ChlN/ChlB)2; e, (ChlN/ChlB)2 and ChlL2 after oxygen exposure; f, lysis buffer. E, circular dichroism spectra of ChlL2 in the presence and absence of nucleotides. Spectrum a, ChlL2 (85 μm) + 2 mm MgATP; spectrum b, ChlL2 (85 μm) + 2 mm MgADP; spectrum c, sole ChlL2 (85 μm).