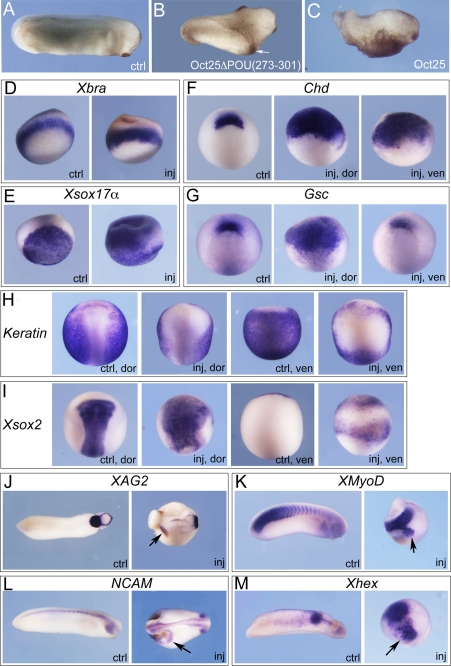
FIGURE 2.
Oct25ΔPOU(273–301) mutant reveals a strong dorsalizing activity in embryos. A and B, injection of a total of 1 ng of Oct25ΔPOU(273–301) RNA into two ventral blastomeres at the four-cell stage leads to formation of partial secondary axes (indicated with arrow in B) as compared with an uninjected control (ctrl) embryo (A). C, ventral injection of 800 pg of wild type Oct25 RNA leads to suppression of posterior structures. d–M, characterization of the resulting phenotype by whole mount in situ hybridization for selected marker genes. A total of 1 ng of RNA was injected into either two dorsal blastomeres or two ventral blastomeres at the four-cell stage as indicated for phenotype analyses. D, the pan-mesodermal marker gene Xbra is not altered significantly. E, ectopic expression of the endodermal gene Xsox17α in the marginal zone and the ectoderm. F, during gastrulation, Chordin (Chd) expression is detected in an uninjected control embryo (ctrl) at the dorsal blastopore lip. In an embryo with dorsal injection of Oct25ΔPOU(273–301) RNA, the expression domain of Chd is highly expanded (inj, dor). Moreover, Chd is also ectopically induced at the ventral side upon ventral injection (inj, ven). G, at gastrula stage, Goosecoid (Gsc) is also expressed in the dorsal lip (ctrl); dorsal injection of Oct25ΔPOU(273–301) RNA up-regulates Gsc transcription significantly (inj, dor), but ventral injection does not induce ectopic expression at the ventral side (inj, ven). H, at neurula stage, expression of epidermal keratin (keratin) is detected throughout the epidermis excluding the neural fold (ctrl, dor; ctrl, ven). In contrast, it is severely reduced in both the dorsal (inj, dor) and ventral side (inj, ven) in response to injection of Oct25ΔPOU(273–301) RNA. I, neural fold marker Xsox2 is strongly increased in response to dorsal injection of the Oct25 mutant RNA (inj, dor), and ectopic expression is observed in response to ventral injection (inj, ven) compared with uninjected embryos (ctrl, dor; ctrl, ven). J, during tailbud stage, injection of Oct25ΔPOU(273–301) RNA causes ectopic expression of XAG2, a gene that marks the most anterior structure, i.e. the cement gland. K, ectopic formation of somites is observed in injected embryos, as indicated by XMyoD expression. L, ectopic formation of neural tissue as indicated by NCAM expression. M, ectopic anterior endoderm formation, as revealed by ectopic expression of Xhex in addition to its regular expression domain. Arrows indicate ectopic gene expression.