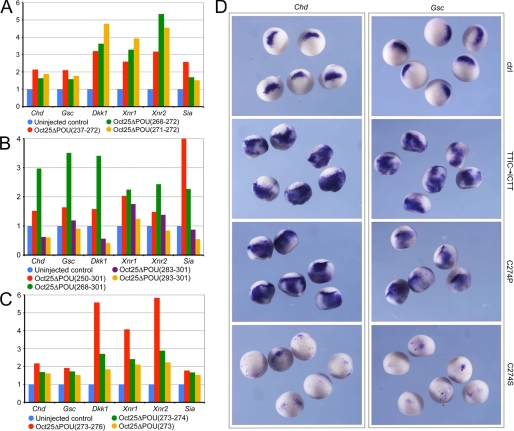
FIGURE 6.
Mutations of single amino acids cause reversal of Oct25 function and lead to an up-regulation of dorsal mesodermal genes. A, Oct25 mutants with N-terminal deletion of the POU-specific domain (aa 237–272), a few amino acids (aa 268–272), or only two amino acids (aa 271–272) cause prominent up-regulation of gene transcription in embryos. B, Oct25 mutants with depletion of a broad region of the POU-specific domain (aa 250–301 or 268–301) also have a stimulating effect on gene transcription. When a small region close to the C terminus of the POU-specific domain (aa 283–301) is truncated, this mutant exhibits either no or only rather weak stimulating activity. Up-regulation is completely lost when aa 293–301 are deleted. C, deletion of four amino acids (aa 273–276), two amino acids (aa 273–274), or a single amino acid (aa 273) leads to a strong up-regulation of gene transcription. D, whole mount in situ hybridizations demonstrate that either the change in the order of the four amino acids TTIC to ICTT (TTIC → ICTT) or the mutation of the amino acid Cys-274 to Pro (C274P) lead to an up-regulation of the transcription of Chd and Gsc. When Cys-274 is mutated to Ser, the resulting mutant represses expression of these two genes. RNA for each mutant was injected at a total of 1 ng per embryo, except for Oct25(C274S) RNA, which was injected at a total dose of 300 pg per embryo. ctrl, control.