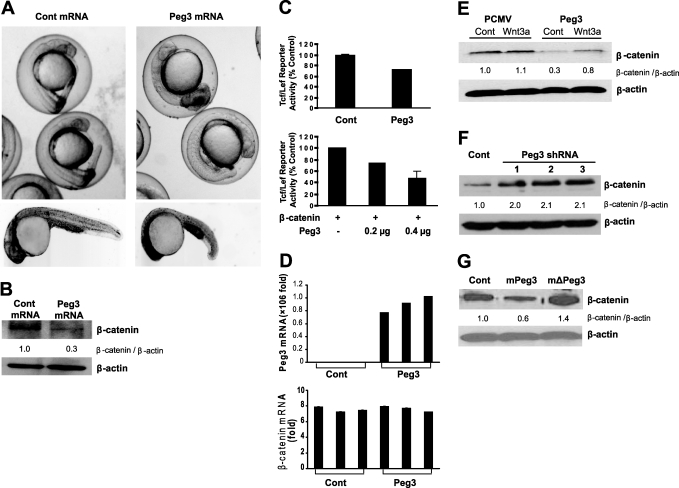
FIGURE 1.
A, zebrafish embryos injected with human PEG3 mRNA at the single-cell stage and allowed to develop for 24 h. Data from intact (upper panels) and dechorionated (lower panels) embryos are shown. Note the defect in tail development after PEG3 mRNA overexpression. B, Western blot analysis illustrating the effect of PEG3 mRNA or noncoding control (Cont) mRNA overexpression on β-catenin protein levels in zebrafish embryos after 24 h of development. β-Actin was used as a loading reference. C, Tcf/Lef1 luciferase reporter assay in 293T cells after Peg3/Pw1 and/or β-catenin overexpression. Data shown are means ± S.E. D, real-time PCR of PEG3 and β-catenin mRNAs after Peg3/Pw1 protein overexpression in 293T cells. Data shown are means ± S.E. E, effect of overexpression of the HA-Peg3/Pw1 vector or a control vector (pCMV) on β-catenin protein expression in 293T cells under control conditions or after Wnt3a (50 ng/ml) exposure. F, Western blot illustrating the effect of Peg3/Pw1 knockdown on β-catenin in 293T cells using three separate Peg3/Pw1 shRNAs. G, Western blot illustrating the effect of mouse Peg3/Pw1 (mPeg3), mouse dominant-negative Peg3/Pw1 (mΔPeg3), or a control vector on endogenous human β-catenin protein expression in HeLa cells.