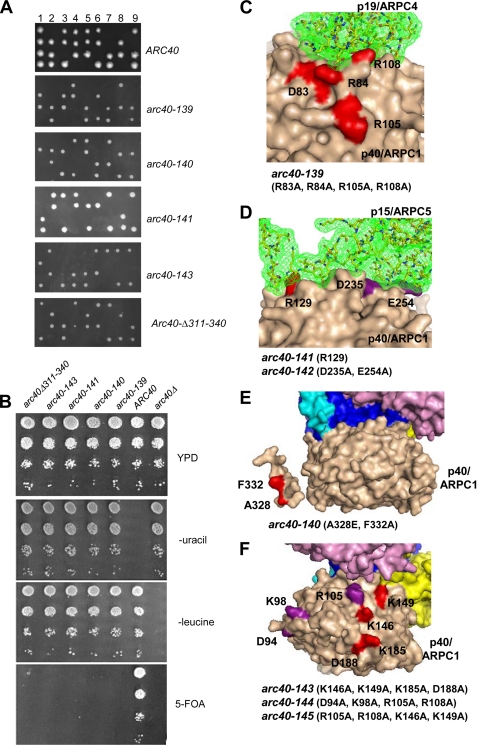
FIGURE 3.
Analysis of lethal arc40 alleles. S. cerevisiae numbering of residues is used in C–F. All of the subunits in the Arp2/3 complex are colored as in Fig. 2A. A, tetrad analysis of arc40 alleles integrated at the LEU2 locus in the heterozygous diploid strain arc40Δ::HIS3/ARC40. The diploid strains were sporulated, and tetrads were dissected. The specific patterns of growth for all alleles except ARC40 indicate lethality (see “Results”). B, cell growth phenotypes of an ARC40 strain and arc40Δ::HIS3 strains with integrated LEU2-marked copies of arc40Δ or specific arc40 alleles carrying a URA3 marked ARC40 plasmid. The cells were grown in YPD medium overnight and then serially diluted, plated on YPD, −uracil, −leucine, or 5-fluoroorotic acid-containing medium, and grown for 3 days at 25 °C. C, surface rendered structure of p40/ARPC1 (tan) showing its contacts with p19/ARPC4 (stick model with green mesh). Residues mutated in lethal arc40-139 are highlighted in red and numbered. D, surface rendered structure of p40/ARPC1 showing contacts with p15/ARPC5, with residues in lethal arc40-141 highlighted in red. Residues in nonlethal arc40-142 are highlighted in purple. E, surface rendered structure of p40/ARPC1 (tan) with residues in lethal arc40-140 highlighted in red. F, surface rendered structure of p40/ARPC1 (tan) displaying residues that have been predicted to mediate mother filament side binding (17). Mutated residues that when combined yielded a lethal allele (arc40-143) are highlighted in red. Residues that when combined were pseudo-wild type are highlighted in purple.