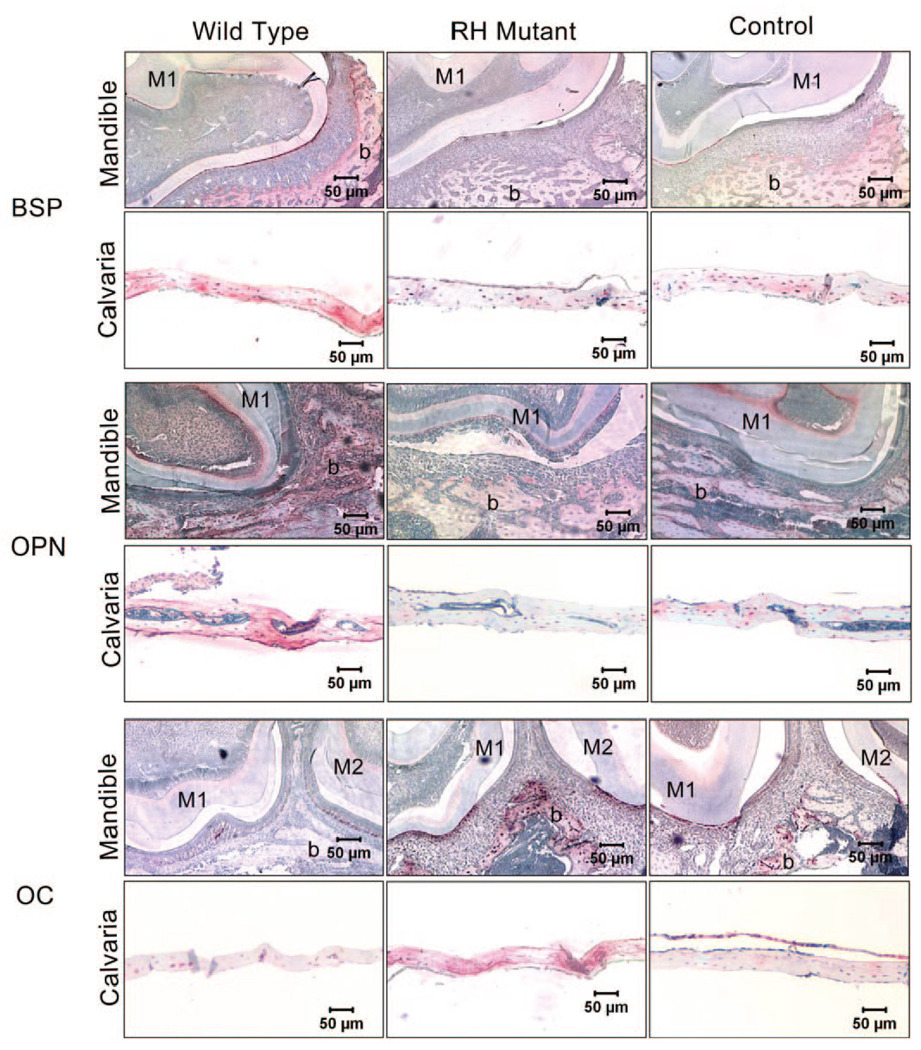
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemical analysis of extracellular matrix proteins OPN, BSP, and OC in bone tissues of BSP/TVA overexpressing mutated Dlx5 (RH mutant), wild-type Dlx5 (Wild-type), and empty vector (Control). Nine days after infection of BSP/TVA with viral constructs, bones were isolated, and immunohistochemistry was performed to determine the expression of OPN, BSP, and OC in calvarial and mandibular tissues. Expression levels of OPN, BSP, and OC in mandibles were shown in transverse sections of the developing first and/or second molars and the surrounding tissues at the cementumenamel junction. In control mandibular tissues, BSP and OCN were both moderately expressed in the cells (osteoblasts and osteocytes) and in bone matrix associated with the alveolar bone surface. BSP expression in mandibular tissues isolated from the wild-type group was up-regulated in the alveolar bone surface area, and moderate expression can be detected in the odontoblast layer. However, BSP expression in mandibular tissues isolated from RH mutant group was down-regulated, and there is no evident BSP expression above background. In contrast, OCN expression in the wild-type group was weaker than that in the RH mutant group. OPN expression in control mandibular tissues can also be detected in the alveolar bone surface (osteoblasts, osteocytes, and bone matrix), as well as the odontoblast layer. OPN expression in the corresponding areas in the wild-type group and the RH mutant group was up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively. Expressions of BSP, OPN, and OCN are all evident in the osteocytes and bone matrix of control calvarial tissues. While BSP and OPN expression levels are increased in the wild-type group and decreased in the RH mutant group, OCN expression level is down-regulated in the wild-type group and up-regulated in the RH mutant group. M1, the first mandibular molar; M2, the second mandibular molar; b, bone.