Figure 1.
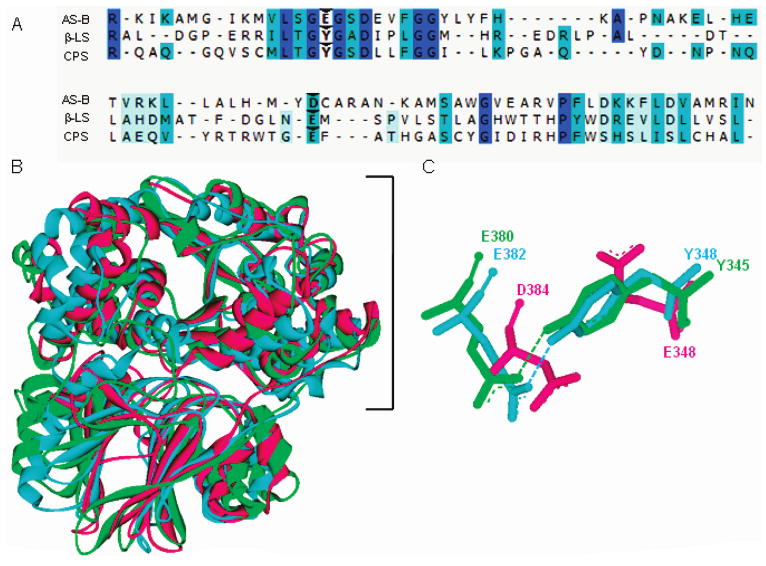
Sequence and structural comparison of homologues AS-B, β-LS, and CPS. Panel A gives a partial sequence alignment of AS-B, β-LS, and CPS with weak to identical matches in amino acid sequence shown as light blue to dark blue, respectively. Carets indicate the conserved carboxylate-containing residues (D384, E382, E380) and the replacement of AS-B E348 with Y348 and Y345 in β-LS and CPS, respectively. Panel B depicts the structural superimposition of AS-B, β-LS, and CPS monomers with the synthetase domains enclosed by a bracket. Panel C illustrates the conserved Tyr-Glu dyads in β-LS and CPS overlaid with the coaligning aspartate and catalytic glutamate in E. coli AS-B. Panels B and C illustrate AS-B, β-LS, and CPS as the colors pink, blue, and green, respectively.
