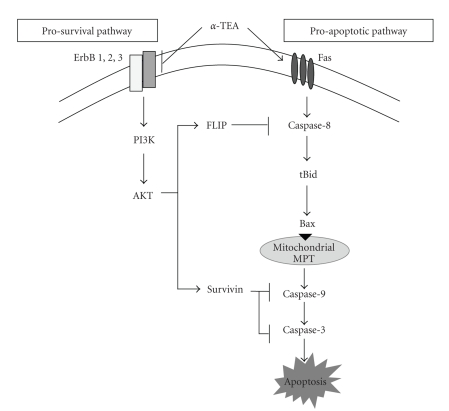
Figure 6.
Schematic of signaling pathways involved in α-TEA-induced apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cell lines. Based on previously reported data [27] and data reported here, we propose both blockage of prosurvival and activation of proapoptotic signaling pathways are involved in α-TEA-induced apoptosis of human ovarian cancer cell lines. α-TEA triggers activation of the proapoptotic Fas (CD95) pathway, leading to a caspase-8- and mitochondria/caspase-9-dependent proapoptotic cascade [27]. Additionally, α-TEA downregulates ErbB1 (in the A2780/CP70R cells) and ErbB2 and ErbB3 in both A2780 and A2780/CP70R cell lines, leading to suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling and expression of the downstream antiapoptotic factors FLIP and survivin, which potentiates the α-TEA-induced proapoptotic cascade via enhancing the activation of caspase-8 and caspase-9/3, respectively, [15–17].