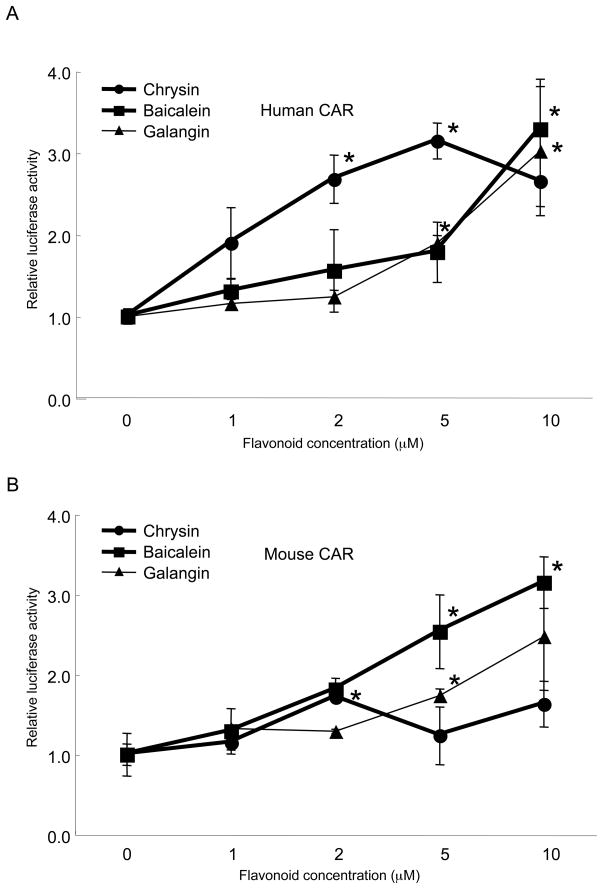
Figure 3. Dose-dependent activation of CAR by flavonoids.
Chrysin, baicalein and galangin were examined for their ability to activate human (A) and mouse (B) CAR in a dose-dependent manner. Significant increase of realative luciferase activity compared to DMSO controls were marked by asterisks (Welch's t-test, P < 0.05, n=3). In contrast to chrysin, which showed maximum CAR activation at 5 μM, baicalein and galangin showed constant increases in CAR response in a dose-dependent manner at 10 μM and below.