Figure 2.
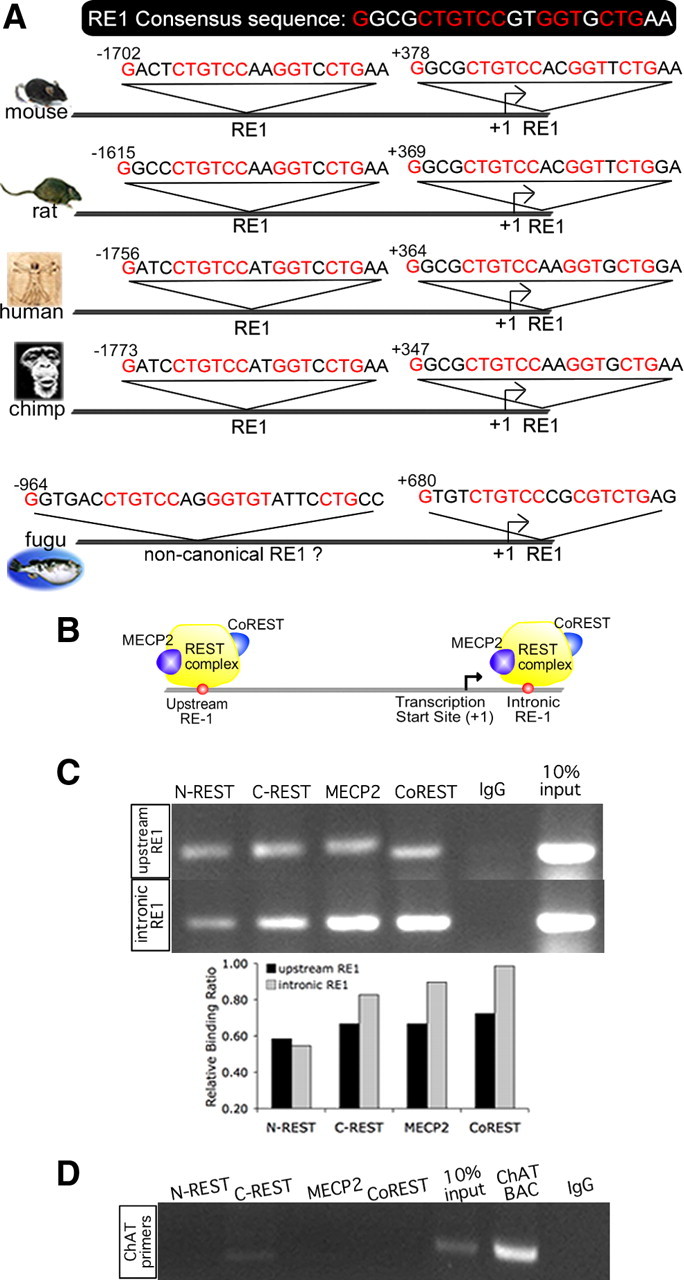
Conservation of sequence and position of a novel RE-1 site located upstream of the TSS of mouse Kcc2b; upstream and intronic RE-1 bind to REST complex. A, Upstream and intronic RE-1 sites of mammalian species (mouse, rat, human, and chimpanzee) are highly similar in sequence to consensus RE-1 (Schoenherr et al., 1996). Positions of the RE-1 sequences are indicated relative to TSS, showing a preservation of position for the dual RE-1 in mammals as well. Predicted RE-1 sites of a nonmammalian vertebrate, the pufferfish Takifugu rubripes, are also shown, indicating a canonical intronic RE-1 and a noncanonical upstream site. B, Schematic showing REST complex–RE-1 binding interaction at the Kcc2b promoter. C, ChIP was conducted using N2A neuronal cells and antibodies against N- and C-REST and corepressor proteins MECP2 and Co-REST. Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR amplified using primers that flank the upstream and intronic RE-1 sites. Bar diagram depicts results of band densitometry. D, Results of the control ChIP PCR are depicted, using primer sequences specific for choline acetyltransferase, a gene without RE-1 sites.
