Figure 4.
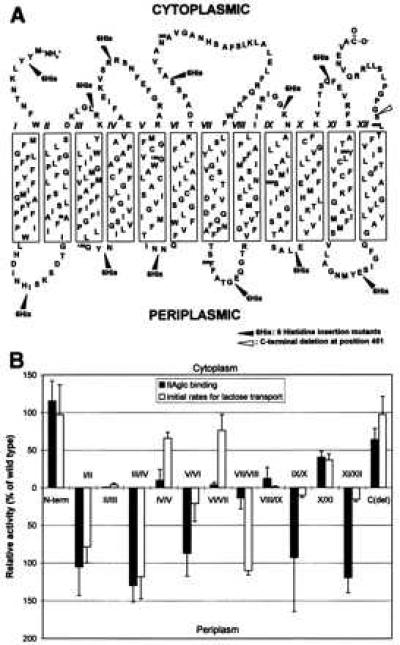
Binding of IIAglc to lactose permease insertion and deletion mutants. In A, the secondary-structure model of E. coli lac permease is shown with 12 6-histidine insertion sites (solid arrowheads) and one C-terminal deletion site (open arrowhead) in the polypeptide chain. The single-letter amino acid code is used, and the 12 putative transmembrane helices are shown in boxes. The model is based on the combination of the hydropathy plot of the primary amino acid sequence of lac permease (10) and some experimental refinements (11). In B, the effect of mutations of lactose permease on the TDG-dependent binding of IIAglc (▪) was compared with that on the initial rates of lactose transport (not normalized) of the permease (□). Expression levels of lac permease from each strain (except the C-terminal deletion mutation) were determined and the binding activity to EIIAglc was corrected as described in the legend to Fig. 3. Because the antibody used for quantitation of expression of lac permease is directed against the C terminus (21), it was not possible to quantitate permease expression in the C-terminal deletion. Consequently, the binding observed in that construct (63% of the control) was not corrected for the level of expression. Therefore, it is likely that the C-terminal deletion is unaffected with respect to IIAglc binding. Binding assays were done three to five times and SDs were plotted. The initial rates for lactose transport of the lac permease mutants came from a previous report (17) and are also expressed as the percentage of wild-type activity.
