Figure 1.
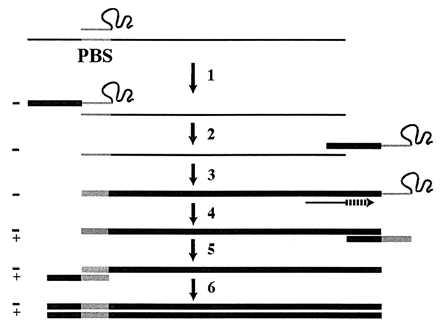
Current model of retroviral replication. (Step 1) After annealing of the tRNA primer to the PBS, RT extends the 3′ end of the tRNA by using the genomic RNA (thin line) as a template to synthesize (−)SS cDNA (thick line) and degrades the RNA template. (Step 2) By virtue of base pair complementarity, the (−)SS cDNA translocates to the 3′ end of the RNA genome. (Step 3) Nearly full-length −cDNA is synthesized, terminating at the PBS. (Step 4) Strong-stop plus-strand cDNA synthesis is initiated from an RNaseH-resistant polypurine tract in the viral RNA. During this step, the 3′ 18 nt of the tRNA primer are copied. (Step 5) Base pair complementarity between the strong-stop plus-strand cDNA and the −cDNA mediates the second strand transfer. (Step 6) Completion of full-length double-stranded proviral cDNA synthesis by RT.
