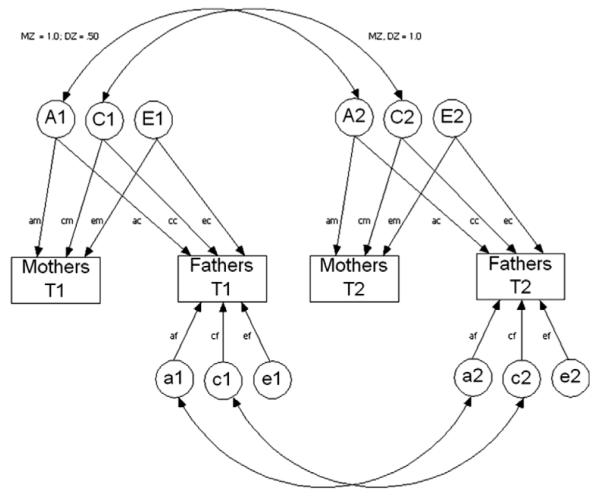
Fig. 2.
A bivariate Cholesky decomposition was used to partition the variances of, and covariances between, mothers’ reports and fathers’ reports into genetic and non-genetic components. Separate models were estimated for Effortful Control, Negative Affectivity, and Surgency/Extraversion factors. Latent variables represent overlapping additive genetic effects (A), additive shared environment effects (C), and additive non-shared environment effects including error (E), as well as residual genetic (a), shared environmental (c), and non-shared environmental (e) variance. In this model, the pathways between latent variables representing genetic variance and covariance across twins are set at 1 for monozygotic (MZ, identical) twins and .5 for dizygotic (DZ, fraternal) twins. The pathways for shared environmental variance and covariance across twins are set at 1 for MZ and DZ twins, whereas the pathways for non-shared environmental variance and covariance across twins are set at 0 for MZ and DZ twins.