Figure 1.
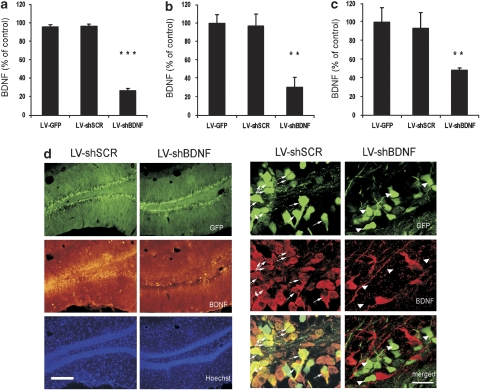
Validation of LV-shBDNF infection and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) knockdown (KD) in vitro and in vivo. BDNF protein expression was measured in a C6 rat glioma cell line and in vivo in response to infection with lentiviral vector (LV) expressing either green fluorescent protein (GFP) only (LV-GFP; infection control), scrambled shRNA (LV-shSCR; shRNA control) or shRNA complementary to the coding axon of the rat BDNF gene (LV-shBDNF; active sequence). Panel a presents BDNF levels measured in a C6 cell medium 48 h after infection and normalized per 106 cell number. Data are presented as percentages of BDNF secreted from noninfected control cells. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) reveals a significant main effect of treatment (F(3, 20)=374.756, P<0.001). Differences between the various LV treatments were assessed using Fisher post hoc analysis (***P<0.001; n=6 per treatment). Panel b presents BDNF levels in the dentate gyrus (DG) measured by immunohistochemistry and epifluorescence microscopy. The intensity per unit area was measured for each slice. BDNF levels are expressed as a percentage of control, by measuring the intensity in slices taken from infected rats relative to control slices taken from the noninfected rats. One-way ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of treatment (F(3, 17)=29.926, P<0.01). Differences between control and infected brains were assessed using Fisher post hoc analysis (**P<0.01; n=5 to 6 per group). Panel c presents BDNF levels in the dDG measured by ELISA and normalized per total protein. BDNF levels are expressed as a percentage of control. One-way ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of treatment (F(3, 14)=5.868, P<0.01). Differences between control and infected brains were assessed using Fisher post hoc analysis (**P<0.01; n=4 or 5 per group). Panel d presents representative micrographs of hippocampal slices including the dDG from the rats injected with LV-shSCR (control) or LV-shBDNF (BDNF KD). The micrographs in the left present the infection spread based on the GFP expression (green) within the sections. BDNF protein expression was visualized by immunohistochemical staining (middle lane). Note the significant reduction in BDNF expression induced by the LV-shBDNF microinjection. Cell nuclei were visualized using Hoechst staining (lower lane). The micrographs on the right show a higher magnification of an infected hippocampal region. The upper lane shows GFP expression as an infection marker, whereas the middle lane shows BDNF protein staining. The lower lane shows superimposition of the upper and middle lanes to highlight cells expressing both GFP and BDNF. The arrows highlight that while the rat brain infected with LV-shSCR show BDNF expression within infected (GFP) cells, none of the infected cells in the LV-shBDNF rat brain show BDNF expression. Scale bar=200 μm at the left micrographs and 20 μm at the right micrographs.