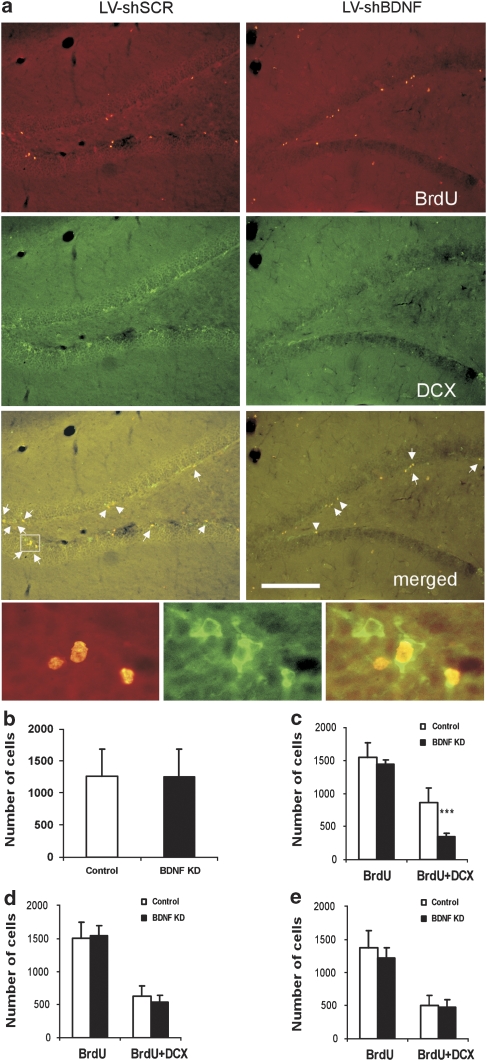
Figure 5.
The effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) knockdown on hippocampal neurogenesis. Neurogenesis in the subgranular zone (SGZ) was measured 2 months after the induction of BDNF knockdown (KD) in the dorsal dentate gyrus (dDG), CA3 or ventral subiculum (vSUB) of mature rats. Rats were injected intraperitoneally with 50 mg kg−1 bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) at 12 h intervals for 2 days. Twenty-four hours or a week later rats were deeply anesthetized and transcardially perfused. Immunohistochemistry was performed to detect neuronal dividing cells by counting the cells that incorporated BrdU into their genome, and express the immature neuronal marker doublecortin X (DCX), as shown in the small micrographs. Representative micrographs of the dDG from rats injected with lentiviral vector (LV)-shSCR (Control) or LV-shBDNF (BDNF KD) into their dDG are presented in panel a. Proliferation was measured by counting BrdU-stained cells (upper lane), immature neurons were visualized by DCX (middle lane), and differentiation was measured by counting double-labeled BrdU and DCX cells (lower lane). Scale bar=200 μm. Panel b shows a quantitative analysis of proliferation comparing control and BDNF KD rats after LV infections in the dDG. This panel presents data from rats that were euthanized 24 h after BrdU injections. Panels c,d and e show a quantitative analysis of proliferation and differentiation comparing control and BDNF KD rats after LV infections in the dDG, CA3 or vSUB, respectively. These rats were injected with BrdU a week before euthanasia. A significant effect of BDNF KD was observed only in the dDG group and only in the number of differentiated neuronal cells (BrdU + DCX) (t(11)=5.672, P<0.001), but not in total proliferation (BrdU). Values are mean±s.e.m. (*** P<0.001, n=6–9 per group).