Figure 1.
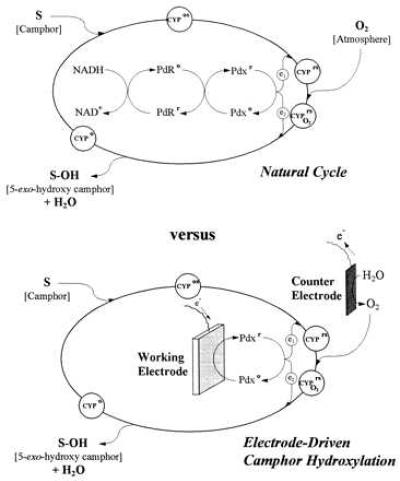
Natural (Upper) and direct-electrode-driven (Lower) catalytic cycles for substrate (camphor) hydroxylation by the P450cam monooxygenase system. Substrate binds with the oxidized form of cytochrome hemoprotein CYP101 (P450cam) to form the protein complex CYPos, which receives the first electron e1 from reduced putidaredoxin Pdxr. Dissolved oxygen is bound in the natural cycle to form the complex CYPO2rs, which receives a second electron e2 from Pdxr, whereupon the complex decomposes to give the stereospecifically hydroxylated product (5-exo-hydroxy-camphor). In the electrode-driven process, a semiconductor working electrode supplies reducing power to oxidized putidaredoxin Pdxo, replacing NADH and putidaredoxin reductase PdR as reducing components. Also, oxygen is generated electrochemically at a controlled surface area counter electrode in an anaerobic bioreactor.
