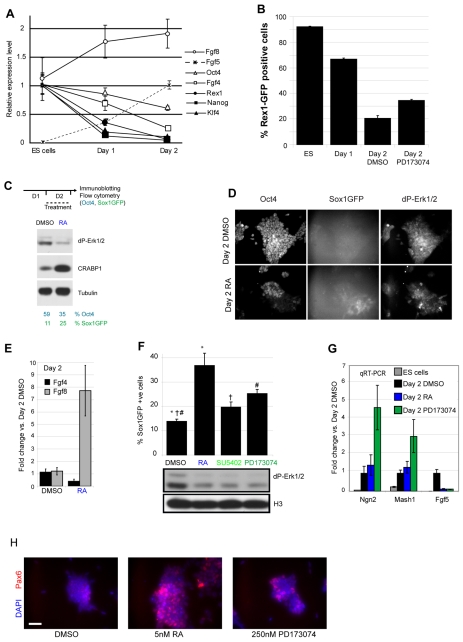
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of Fgf signalling mimics retinoid induction of neural differentiation. (A) Gene expression profile of key genes during monolayer differentiation relative to expression in undifferentiated ES cells (for Fgf5 relative to expression at day 2). Transcript levels in ES cells and at day 1 are significantly different for all genes (P<0.05), except Oct4, Fgf4 and Fgf8, comparison of levels in ES cells and at day 2 for Oct4 and Fgf4 are P<0.05 and 0.06, respectively. Data are means ±s.e.m. from a representative experiment performed in triplicate. (B) Rex1-GFP cells in N2B27, analysed by flow cytometry. PD173074 treatment during day 2 increases Rex1-GFP+ cells compared to control (DMSO), suggesting a reversion of some cells to the pluripotent state. Results are means of two experiments performed in triplicate +s.e.m. All pairs of treatments are significantly different (P<0.05). (C) RA treatment for 24 hours during day 2 causes a decrease in dP-Erk and induction of Crabp1 [an RA-responsive gene (Lane et al., 2008)] by western blotting, but a decrease in Oct4-positive cells and an increase in Sox1-positive cells as analysed by flow cytometry. Results are representative of three experiments performed in triplicate ±s.e.m. (D) Cells labelled for Oct4, dP-Erk1/2 and Sox1-GFP, following day 2 treatment. RA treatment reduced dP-Erk and Oct4 levels, but increased the number of Sox1-GFP-positive cells. (E) At the end of day 2, RA causes a further decrease in Fgf4 and increase in Fgf8, data from two independent experiments performed in triplicate. (F) On day 2, treatment with RA or Fgfr inhibitors (PD173074 or SU5402) reduces levels of dP-Erk and increases the number of Sox1-GFP-positive cells. Symbols indicate statistically significant differences between treatments at P<0.05 (paired t-test, n=5 independent experiments performed in triplicate). (G) Fgfr inhibition or RA treatment on day 2 causes a decrease in Fgf5 transcripts and an increase neural progenitor markers Ngn2 and Mash1 (P<0.05), except for RA-induction of proneural genes, which was only statistically significant on exposure to 50 nM RA (Ngn2, P<0.05). Results are averages of three experiments performed in triplicate ±s.e.m. (H) Following day 2 treatment, cells were labelled with an antibody against Pax6. Both RA and PD173074 cause an increase in the number of Pax6-positive cells, with RA having a stronger effect. Result is representative of five randomly selected fields. Scale bars: 50 μm.