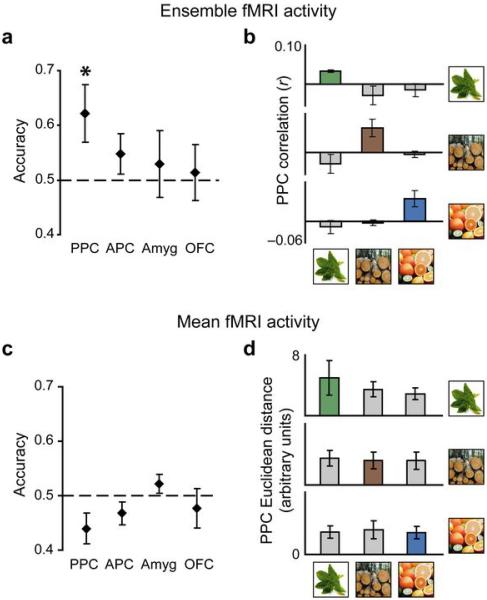
Fig. 6.
fMRI pattern discrimination of odor categorical perception in PPC. (a, b) Classification performance calculated using fMRI patterns of ensemble activity. (a) Odor identification accuracy (mean ± between-subjects s.e.m; N = 4) was significantly greater than chance in PPC only. *, P < 0.05. (b) The within-category correlation was greater than the across-category correlation in PPC for all three odor quality categories, an effect that was separately observed for each category. (c, d) Classification performance calculated using fMRI mean activity. (c) Identification accuracy did not significantly differ from chance in any of the four regions, and there was no significant group difference between within-category and across-category Euclidean distances in PPC (d), or in APC, amygdala, or OFC (data not shown).