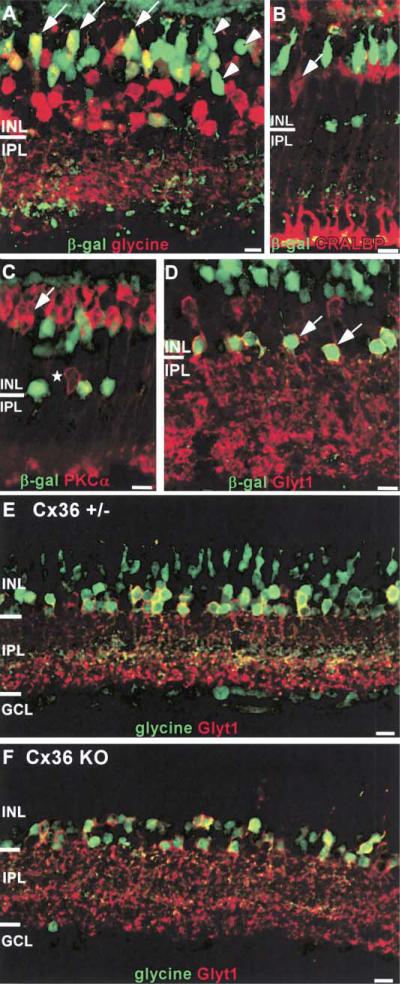
Figure 4. Identification of β-Gal-Positive Neurons in the INL.
(A) Some β-gal-positive bipolar cells colocalize with glycine, indicating Cx36 expression in On CBs (examples indicated with arrows). However, β-gal-positive bipolar cells without glycine indicate Cx36 expression by another type of CB (examples indicated by arrowheads).
(B and C) Muller glia and rod bipolar cells do not express β-gal. β-gal-positive neurons in the bipolar cell layer do not colocalize with the Muller glia marker CRALBP or the RBC marker PKCα. PKCα also labels a small number of amacrine cells (star) that do not overlap with the β-gal-positive amacrine cells.
(D) In Cx36+/– mice, β-gal-positive amacrine cells located at the most vitreal edge of the INL also colocalize with GLYT1 (examples indicated with arrows), confirming the identification of these cells as AII amacrines.
(E and F) Glycine is readily detected in +/– (E) but not KO (F) bipolar cells, suggesting that the gap junctions between AII amacrines and On CBs require Cx36. Sections were counterstained for GLYT1 to mark glycinergic amacrines..
Scale bars equal 10 μm.