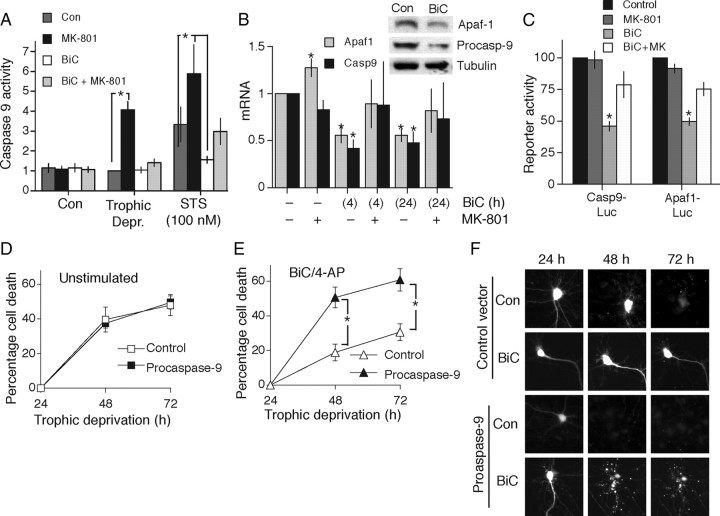
Figure 4.
Synaptic activity suppresses the expression of Apaf-1 and procaspase-9. A, Synaptic NMDAR activity inhibits activation of caspase-9 in response to an apoptotic insult. Neurons were treated with the indicated compounds as described in Figure 1A. Caspase-9 activity was measured after 48 h trophic deprivation, or 16 h staurosporine treatment. *p < 0.05 (n = 4). B, Synaptic NMDAR activity suppresses expression of apoptosome components. QRT-PCR analysis of Apaf1 and Casp9 expression in neurons. *p < 0.05 (n = 4). Inset shows example Western blot illustrating BiC/4-AP-induced suppression of protein expression. C, Promoter regions of Apaf1 and Casp9 confer activity-dependent suppression on a luciferase reporter gene. Neurons were transfected with the indicated reporters, plus a TK-Renilla control vector. At 24 h after transfection, neurons were stimulated for the indicated times and firefly luciferase reporter activity was measured, normalized to the Renilla control. *p < 0.05 (n = 3). D, E, Overexpression of procaspase-9 accelerates apoptosis in AP-bursting but not control neurons. Neurons expressing eGFP plus either a control vector (β globin) or a vector encoding procaspase-9 were placed in trophically deprived medium and either left unstimulated (D) or treated with BiC/4-AP to induce AP bursting (E). Pictures of neurons were taken at 24 h and then their viability was monitored at 24 h intervals. *p < 0.05 (n = 5). F, Example pictures relating to D and E.