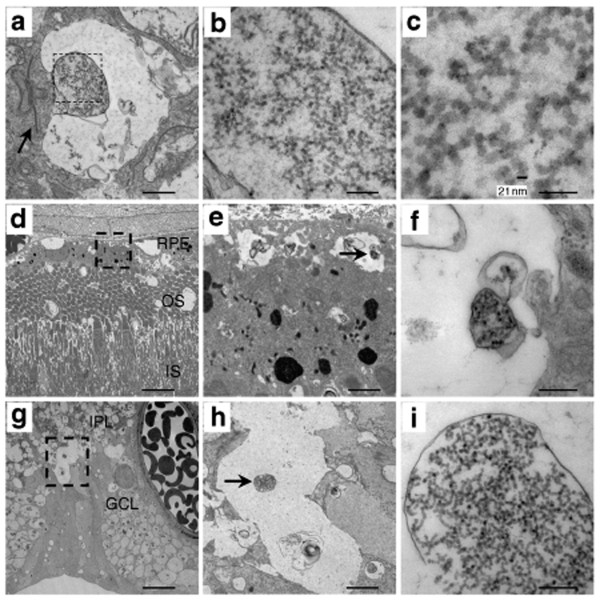
Figure 3.
Detection of adeno-associated viral (AAV) particles in the treated retina of D1. (a–c) Ultrathin sections of the portion of the retina representing the outer nuclear layer at different magnifications. (a) Portion of the retina representing the outer plexiform layer. The arrow indicates a synaptic ribbon structure. The square marks the area of higher magnification in b. Bar = 1 µm. (b) Vector particles are found inside of synaptic invaginations. Bar = 200 nm. (c) Magnification of b to identify the hexagonal structure and the size of the particles of 21 nm. Bar = 100 nm. (d–f) Ultrathin sections of the portion of the retina representing the RPE at different magnifications. (d) Portion of the retina where viral particles are found (indicated by a square). Bar = 20 µm. (e) Magnification of the area indicated in d. Vector particles are found inside closed compartments (indicated by an arrow). Bar = 1 µm. (f) Magnification of e. Bar = 200 nm. (g–i) Ultrathin sections of the portion of the retina representing the ganglion cells. (g) Portion of the retina where viral particles are found (indicated by a square). Bar = 20 µm. (h) Magnification of the area indicated in g. Vector particles are found inside closed compartments. Bar = 2 µm. (i) Magnification of h. Bar = 200 nm. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; OS, outer segments (of photoreceptors); IS, inner segments (of photoreceptors); IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.