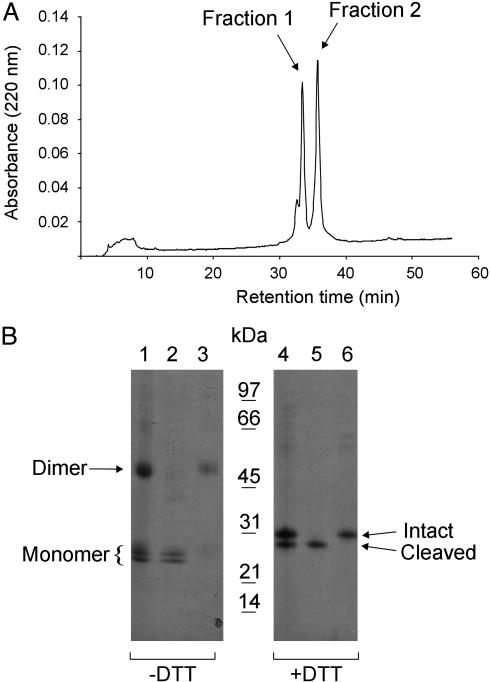
Fig. 1.
Separation of monomeric and dimeric human EC-SOD. (A) Purified EC-SOD was subjected to reversed-phase HPLC by using a C8 column and a shallow gradient of acetonitrile in TFA (0.5% solvent B min–1). The absorption profile at 220 nm is shown, with the two collected peaks indicated. (B) The separated material was analyzed by SDS/PAGE and Coomassie blue staining under nonreducing (–DTT) and reducing (+DTT) conditions as indicated. Lanes 1 and 4 represent purified EC-SOD used for the reversed-phase HPLC separation. Lanes 2 and 5 and lanes 3 and 6 represent the material collected in fractions 1 and 2, respectively. The positions of the disulfide-linked dimer and the monomer (Left) and the intact and cleaved forms under nonreducing conditions (Right) are indicated. A molecular mass marker is shown in the center. The analysis shows that EC-SOD can be separated into monomer and dimer by reversed-phase HPLC.