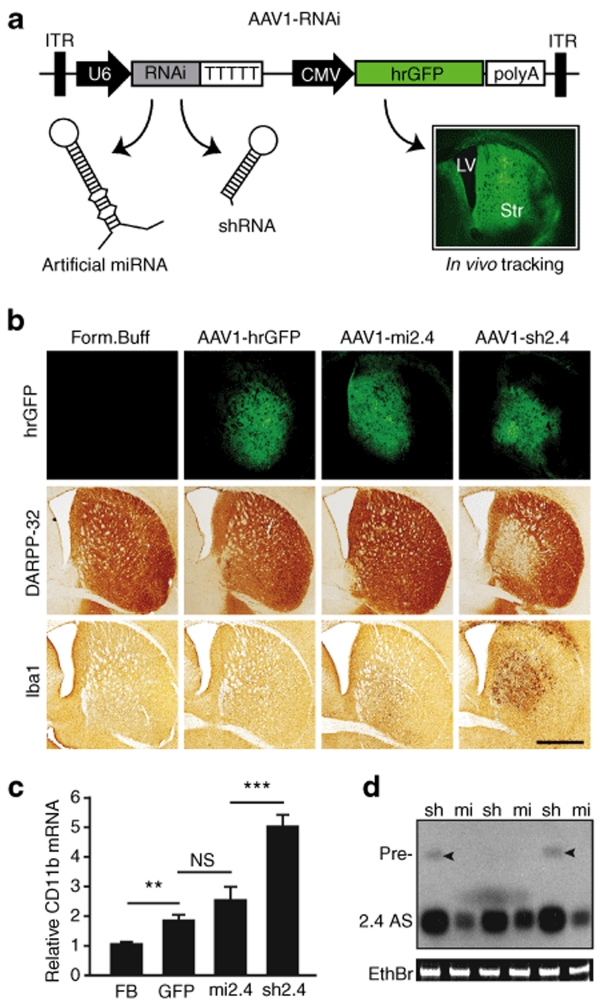
Figure 1.
Mi2.4 demonstrates improved safety, relative to sh2.4, in HD-N171-82Q mice. (a) Diagram of recombinant AAV2/1 viral vectors which express htt-specific RNAi and hrGFP; the latter allows tracking of in vivo transduction within mouse brain (Str = striatum; LV = lateral ventricle). (b) HD-N171-82Q mice were injected with either formulation buffer (FB) or viral vectors into the striatum, and 3 months later, histological analyses were performed to assess for striatal toxicity. Photomicrographs representing hrGFP autofluorescence and immunohistochemical staining of DARPP-32-positive neurons and IbaI-positive microglia are shown for each treatment group. Scale bar = 500 µm for each photomicrograph. (c) Microglial activation was also evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR analyses measuring the endogenous mouse CD11b mRNA levels in striatal RNA samples. Normalized results are shown as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 5; ***, ** and NS indicate P < 0.001, P < 0.01 and no significance, respectively). (d) Small transcript northern blot analysis was performed to assess the levels of htt-specific antisense (2.4 AS) RNA present in AAV1-RNAi-treated striata (sh = sh2.4, mi = mi2.4; n = 3 treated striata). Sh2.4 treatment yielded a build-up of unprocessed precursor RNAs (Pre-, arrowheads) in 2 of 3 samples. Ethidium bromide (EthBr) staining was performed as a loading control. hrGFP, humanized renilla green fluorescent protein; ITR, inverted terminal repeat; RNAi, RNA interference.