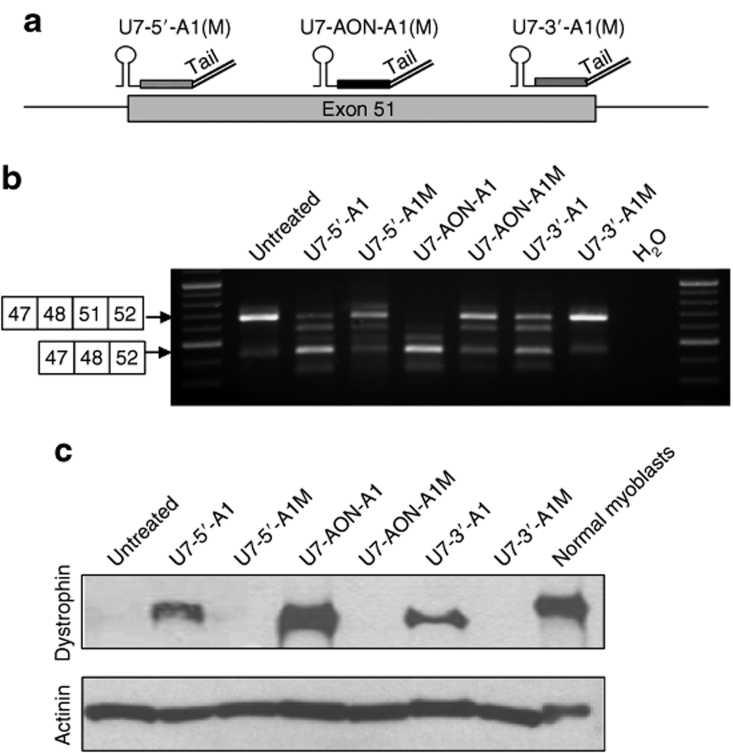
Figure 4.
Comparison of exon 51 skipping in DMD myoblasts induced by bifunctional U7 snRNA depending on their targeted sequence on the exon. (a) Schematic representation of the hybridization of the different U7 snRNA constructs on the exon 51 depending on their antisense sequence. The U7-5′-A1 and U7-5′-A1M carry a complementary sequence to the 5′ of the exon 51 (nt 5–25), whereas the U7-3′-A1 and U7-3′-A1M carry a complementary sequence to the 3′ of the exon 51 (nt 209–229 which corresponds to 5 nt before the end of the exon). The U7-AON-A1 and U7-AON-A1M carry a complementary sequence to a middle exonic splicing enhancer (AON1). (b) DMD myoblasts carrying the Δ49–50 deletion were transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding the different U7 snRNA constructs and exon 51 skipping was assessed by nested reverse transcriptase–PCR. Additional bands due to heteroduplex formation and activation of a cryptic splice site within the exon 51 (previously described34) are visible in same analyses. (c) Western blot probed with dystrophin antibody (top gel) and α-actinin antibody (bottom gel). AON, antisense oligonucleotide; DMD, Duchenne muscular dystrophy.