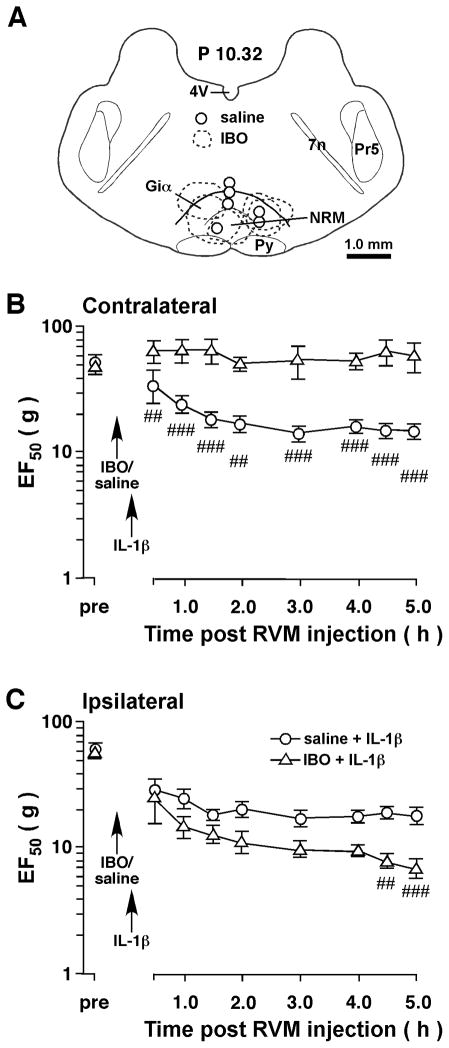
Figure 4.
Intra-RVM ibotenic acid (IBO) attenuated IL-1β-induced contralateral hyperalgesia. Ten-min before a unilateral injection of IL-1β into the Vi/Vc transition zone, IBO (2 μg/0.2 μl, n=5) was microinjected into the RVM to produce excitotoxic neuronal lesions in RVM. Saline was injected as a vehicle control. A. Schematic illustration of the microinjection sites and IBO-produced lesions. The extent of IBO-produced lesions is shown as dashed enclosures. The open circles indicate the injection sites for saline. B. Compared to saline-injected rats, RVM excitotoxic lesions prevented the development of contralateral hyperalgesia after injection of IL-1β into the Vi/Vc transition zone. C. Compared to saline control, there was a slight further decrease in EF50s on the ipsilateral site in the IBO-treated rats. ##, p<0.01, ###, p<0.001, saline vs. IBO (ANOVA with repeated measures and post-hoc test).