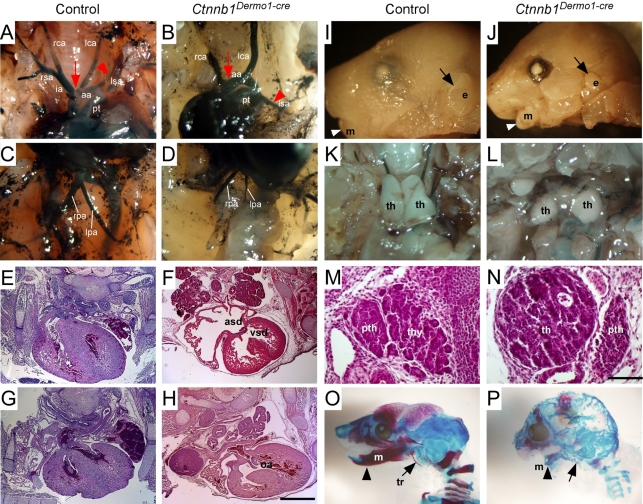
Fig. 2.
Mesenchymal deletion of β-catenin causes DGS-like phenotypes. (A-D) Vascular structure of the aortic arch branches in E16.5 embryos visualized with India ink injection into the left ventricle. (A,C) Control embryo showing a normal branching pattern. (B,D) Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre mutants showing increased separation between the innominate and left common carotid artery (arrow), abnormal origin of the left subclavian artery (arrowhead), and pulmonary artery hypoplasia. (E-H) Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E)-stained sections of E16.5 control (E,G) and Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre (F,H) embryos. Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre embryos showed ventricular and atrial septal defects (F) and overriding aorta (H) anomalies. (I-L) Micrognathia (small mandible, arrowhead) and small outer ear (arrow) in E16.5 Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre (J) compared with control (I) embryos. (K,L) Detached and decreased thymus size in Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre embryos. (M,N) H&E-stained section of the neck region showing normal location of parathyroid gland (pth) next to the thyroid gland (thy) in control (M). Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre embryos (N) showing the parathyroid gland located next to the thymus (th). (O,P) Skeleton preparation stained with Alizarine Red and Alcian Blue showing decreased calcification of cranial bones, missing tympanic ring (arrow) and shortened mandible (arrowhead) in Ctnnb1Dermo1-Cre (P) compared with control (O) embryos. aa, aortic arch; asd, atrial septal defect; e, ear; ia, innominate artery; lca, left common carotid artery; lpa, left pulmonary artery; lsa, left subclavian artery; m, mandible; oa, overriding aorta; pt, pulmonary trunk; pth, parathyroid gland; rca, right common carotid artery; rpa, right pulmonary artery; rsa, right subclavian artery; th, thymus; thy, thyroid gland; tr, tympanic ring; vsd, ventricular septal defect. Scale bars: 200 μm in E-H; 50 μm in M,N.