Fig. 5.
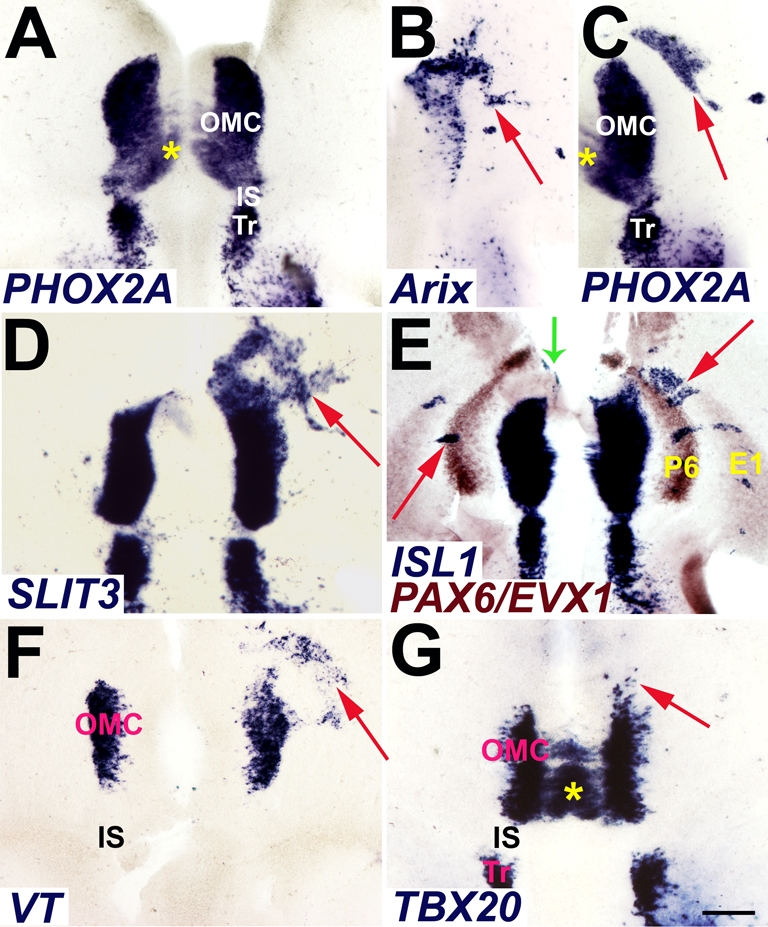
Phox2a induction of OMC gene expression markers. (A) Open-book preparation of E6 chick brainstem whole-mount demonstrates native PHOX2A gene expression in the midbrain OMC and the rostral hindbrain trochlear nucleus (Tr). Rostral is to the top, and the ventricular surface faces the viewer. (B-G) Expression plasmids for rat Phox2a (Arix) were electroporated into E2 chick ventral midbrain and embryos harvested for whole-mount in situ hybridization at E5 (D) and E6 (B,C,E-G). (B) A typical pattern of plasmid delivery by electroporation illustrated in the right midbrain by transgene expression (arrow). (C) Phox2a misexpression elicits induction of endogenous chick PHOX2A (arrow). (D) Phox2a forced expression induces other OMC markers, including the axon guidance molecule SLIT3 (arrow). (E) Lateral arcuate markers PAX6 (P6) and EVX1 (E1) (brown) illustrate the capacity of Phox2a to induce ISL1 (blue) throughout the ventral midbrain (red arrows) and rostrally in caudoventral diencephalon (green arrow). (F,G) Phox2a misexpression induces molecular markers (arrows) of visceral (VT, F) and somatic oculomotor neurons (TBX20, G). Asterisks (A,C,G) mark the contralateral migration of the prospective superior rectus somatic motoneurons (see Chilton and Guthrie, 2004). IS, isthmus. Scale bar: 0.2 mm.
