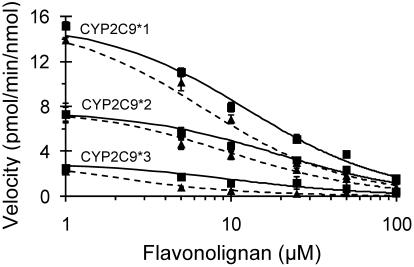
Fig. 4.
Inhibitory effects of silybin A and silybin B on (S)-warfarin 7-hydroxylation activity in recombinant CYP2C9 enzymes. Recombinant enzymes (12.5 pmol/ml) were incubated with (S)-warfarin (4 μM) and a range of concentrations (1–100 μM) of silybin A (■) or silybin B (▴) for 30 (CYP2C9*1 and CYP2C9*2) or 60 (CYP2C9*3) min. Reactions were initiated by the addition of NADPH (1 mM). (S)-Warfarin 7-hydroxylation activity in the presence of vehicle control (0.75% methanol, v/v) was, respectively, 15 ± 1.3, 8.0 ± 0.4, and 3.6 ± 0.3 pmol/min/nmol of recombinant enzyme. Symbols and error bars denote means and S.D., respectively, of triplicate incubations. Solid (silybin A) and dashed (silybin B) curves denote nonlinear least-squares regression of observed values using WinNonlin (version 5.0.1).