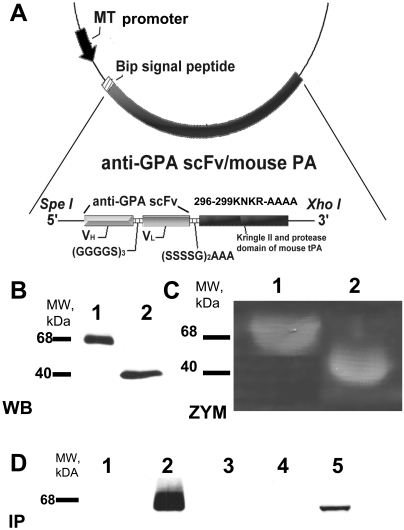
Fig. 1.
Molecular design, expression, and characterization of anti-GPA scFv/PA fusion protein. A, schematic diagram describing the cloning strategy for the fusion construct anti-GPA scFv/PA. Variable domains of the heavy chain and light chains of the antibody were linked by a (Gly4Ser)3 linker and then fused to the N terminus of the kringle II/protease domain fragment of mouse tPA by a (Ser4Gly)2Ala3 linker. The completed construct was then cloned into the SpeI and XhoI sites in the pMT/BIP/V5/HisA expression vector. The DNA fragment encoding kringle II and protease domain of mouse tPA was PCR amplified and cloned into BglII and XhoI sites in the same vector. B, Western blot (WB) analysis of 40 μl of culture medium from S2 cells expressing either anti-GPA scFv/PA fusion protein or PA after induction by 0.5 mM CuSO4. C, casein zymography (ZYM) analysis of culture medium from S2 cells expressing either the anti-GPA scFv/PA fusion protein or the PA after induction by 0.5 mM CuSO4. D, Western blot analysis of protein immunocaptured with mouse (m) or human (h) RBC ghosts: lane 1, lysate of hRBC ghosts incubated in culture medium from S2 cells expressing anti-GPA scFv/PA fusion protein; lane 2, lysate of mRBC ghosts incubated in culture medium from S2 cells expressing anti-GPA scFv/PA fusion protein; lane 3, lysate of hRBC ghosts; lane 4, lysate of mRBC ghosts; lane 5, 40 μl of culture medium from S2 cells expressing anti-GPA scFv/PA fusion protein (positive control).