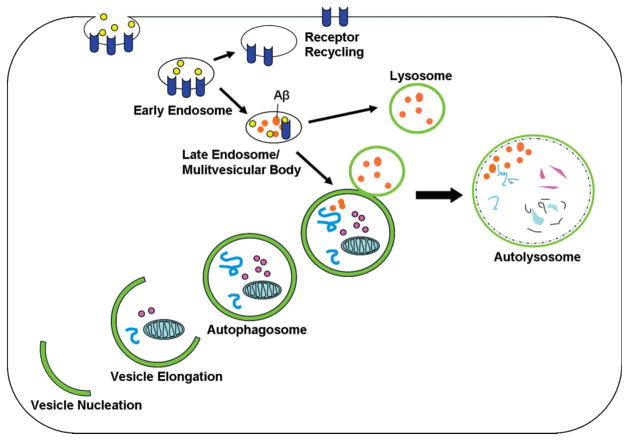
Fig 1.
The endosomal-lysosomal pathway merges with the autophagic pathway. The autophagic pathway is used for organelle and protein turnover. Upon the induction of autophagy, a double-membraned structure, which is called the isolation membrane, forms by vesicle nucleation around cytoplasmic contents and becomes an autophagosome. Cytoplasmic substrates are then degraded after fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome, and this results in the autolysosome. The endosomal pathway, which is important for the uptake and recycling of nutrients and transmembrane receptors, merges with the autophagic pathway. Aβ is generated in multivesicular bodies of the endosomal pathway and may also be generated in autophagosomes. Abbreviation: Aβ, amyloid-β.