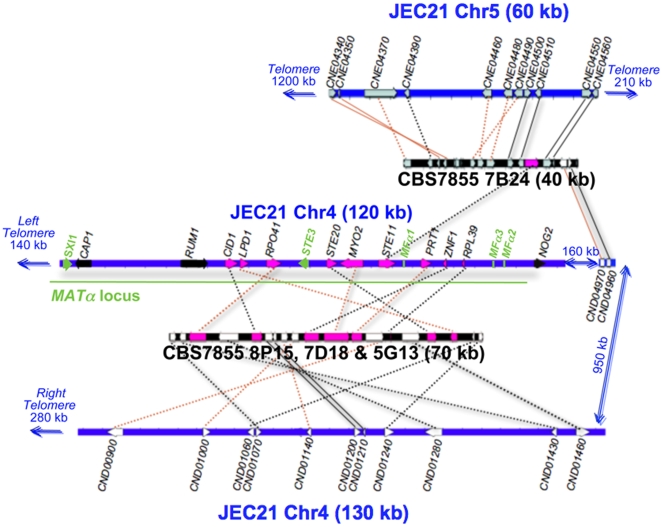
Figure 8. Genomic comparison of MAT-associated genes in C. neoformans.
Several chromosomal translocations, fusions, and inversions appear be present in F. depauperata by comparison to the genome of C. neoformans. Chromosome 4 of C. neoformans var. neoformans strain JEC21 is drawn in blue. Sequenced fosmids from the F. depauperata library of strain CBS7855 are drawn in black. Black lines connect genes in the same orientation, while red lines indicate inversions. Solid lines point to syntenic blocks where the adjacent gene order is conserved. Dotted lines connect orthologous genes where the adjacent genes are not conserved. The aim of this figure is to display the gene arrangements and directions. For simplicity purposes, only those genes present in both species, C. neoformans and F. depauperata, are shown in grey, white, and pink. Genes located on chromosomes 5 and 12 of C. neoformans are shown in grey. Genes located on chromosome 4 of C. neoformans are shown in white while genes associated with the MAT locus of Cryptococcus are shown in pink. The α locus and the mating genes (the pheromone genes MFα, the pheromone receptor gene STE3, and the homeodomain transcription factor SXI1) of C. neoformans are shown in green. Genes shown in black, CAP1 and RUM1, are associated with the MAT locus of C. neoformans, and NOG2 flanks the MAT locus. These three genes were sequenced and identified in F. depauperata, however fosmids containing these genes were not found in the genomic library of F. depauperata.