Figure 7.
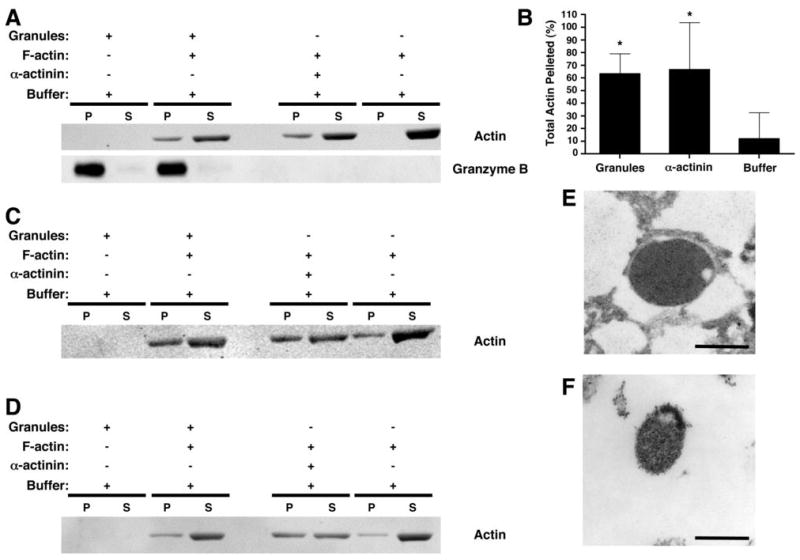
Interaction between myosin IIA-associated lytic granules and F-actin. Lytic granules from an isolated fraction enriched in myosin IIA and granzyme B were prepared from YTS (A–B, E–F), control NK (C), and myosin IIA 1933x patient NK (D) and incubated for 30 min in the presence or absence of F-actin. After centrifugation at 18,000g, the pellet (P) and supernatant (S) were evaluated for actin and granzyme B by Western blot (A, C, D). As a positive control, α-actinin was used to bundle the F-actin, causing it to pellet. Pellet and supernatant from the assay were separated. (B) Percentage of actin in the pellet ±SD from three independent experiments, determined by densitometric analysis. *= p<0.05 compared to buffer (negative control). (E–F) Electron micrographs of lytic granule pellets. The pellet obtained from the mixture of lytic granules and F-actin (E) was compared to the pellet of lytic granules alone (F). Scale bar = 500 nm.
