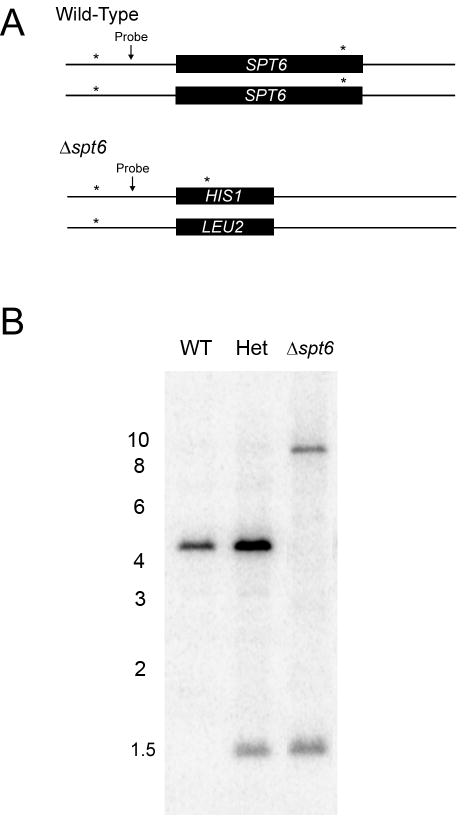
Fig. 3. Southern analysis to confirm homozygous deletion of SPT6 in JMB31.
Genomic DNA was prepared from the wild-type (WT) parent, from the heterozygous strain resulting from replacement of SPT6 with HIS1 (JMB220, Het), and from the strain with both copies of SPT6 replaced by HIS1 and LEU2 respectively (JMB31, Δspt6). Genomic DNA was digested with ScaI and analyzed by Southern blot. Recognition sites for this restriction enzyme exist within the SPT6 ORF, as well as the neighboring upstream and downstream sequences. The gene deletion strategy was predicted to eliminate the ScaI site both within and downstream to the ORF. Panel A shows the predicted ScaI recognition sites (*) and the binding location of the DNA probe. Digestion of wild-type DNA was predicted to yield a 4.2 kb fragment and digestion following replacement with HIS1 predicted a 1.5 kb fragment. SPT6 is adjacent to the telomere of chromosome 7. Because the LEU2 marker does not contain a ScaI site, and the only ScaI site in the region 3′ to the gene was deleted with SPT6, the fragment containing the LEU2 marker was predicted to extend to the telomeric region of the chromosome; ∼ 10 kb. Panel B demonstrates the predicted banding pattern, confirming homozygous deletion of SPT6. Positions of the relevant molecular weight markers (in kb) are depicted.